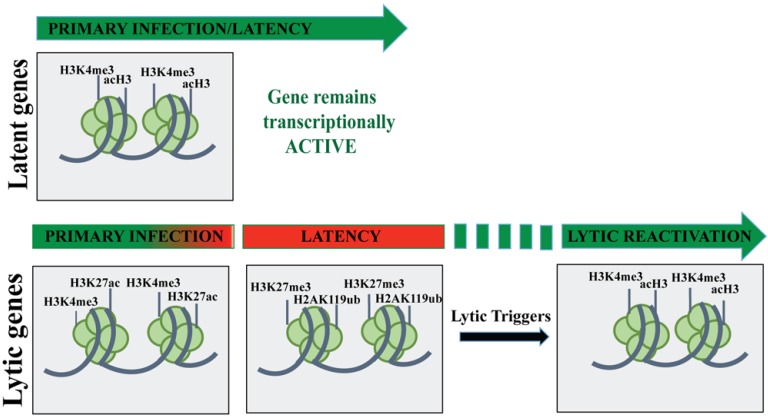
Figure 2.
The chromatin landscape of the KSHV genome during various phases of viral life cycle. Following primary infection, promoters of the key latent genes get epigenetically modified with activating histone marks (H3K4me3/acH3) resulting in the expression of those genes throughout the viral life cycle. In contrast, KSHV lytic gene promoters possess either H3K27Ac/H3K4Me3-rich, active chromatin or H3Ac/H3K4Me3/H3K27Me3-rich bivalent chromatin. During latency, the lytic gene promoters are epigenetically modified with H3K9Me3/H3K27Me3 marks to form a heterochromatin. However, upon reactivation these repressive histone marks are enzymatically removed and gets modified with the activating histone marks (H3K4Me3/H3Ac).