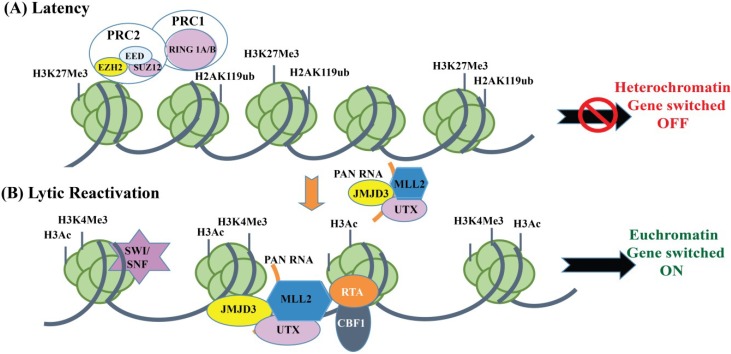
Figure 3.
Polycomb repressive complexes (PRC1 and PRC2) and Polyadenylated RNA-mediated control of KSHV RTA promoter during latency and lytic reactivation. (A) During latency, the histone methyltransferase EZH2 subunit of PRC2 and RING 1A/B subunit of PRC1 bind to the KSHV genome and colocalizes with corresponding repressive histone marks H3K27me3 and H2AK119ub, respectively, leading to silencing of the target genes; (B) Lytic reactivation, triggered by the dissociation of PRC2 and PRC1 from the viral genome or inhibition of EZH2 by chemical compounds, leads to the enrichment of activating histone marks on the viral genome and the activation of gene transcription. PAN RNA, which is highly expressed during lytic reactivation, recruits several cellular and viral chromatin factors (MLL2, JMJD3 and UTX) to the RTA promoter and triggers the expression of immediate early, RTA protein.