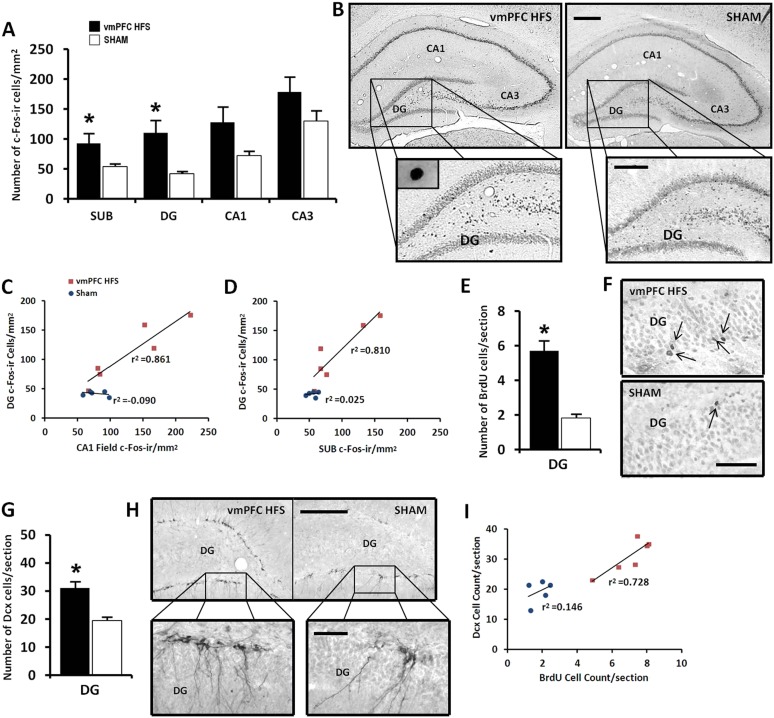
Figure 5. Effects of chronic vmPFC HFS on the hippocampal neuronal activity by c-Fos-ir (A–B) and the morphological changes related to neurogenesis functions (E–I).
Note: VmPFC HFS increased the number of c-Fos-ir positive cells in the subiculum, DG, and a marginal difference (p = 0.059) in the CA1 field of the hippocampus as compared to the sham (A–B; scale bars: 500 μm, low-power magnification; 250 μm, high-power magnification). In neurogenesis-related morphology, after chronic vmPFC HFS, there was an increase of surviving BrdU-positive cells (E–F, scale bar: 500 μm), and neural progenitors—Dcx-positive cells (G–H; scale bars: 300 μm, low-power magnification; 50 μm, high-power magnification). For correlational analysis, there was a strong relationship between the BrdU and Dcx cell-count (I). Importantly, the neurogenic zone of the DG was also highly correlated with the SUB and CA1 field of the hippocampus (C–D), indicating that these regions were functionally associated with memory functions after chronic vmPFC HFS. Abbreviations: SUB, subiculum; DG, dentate gyrus; CA1, CA1 field of the hippocampus; CA3, CA3 field of the hippocampus; vmPFC HFS, high-frequency stimulation of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex; BrdU, 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine; and Dcx, doublecourtin. Indication: *, significant difference from the sham rats, (p < 0.05).