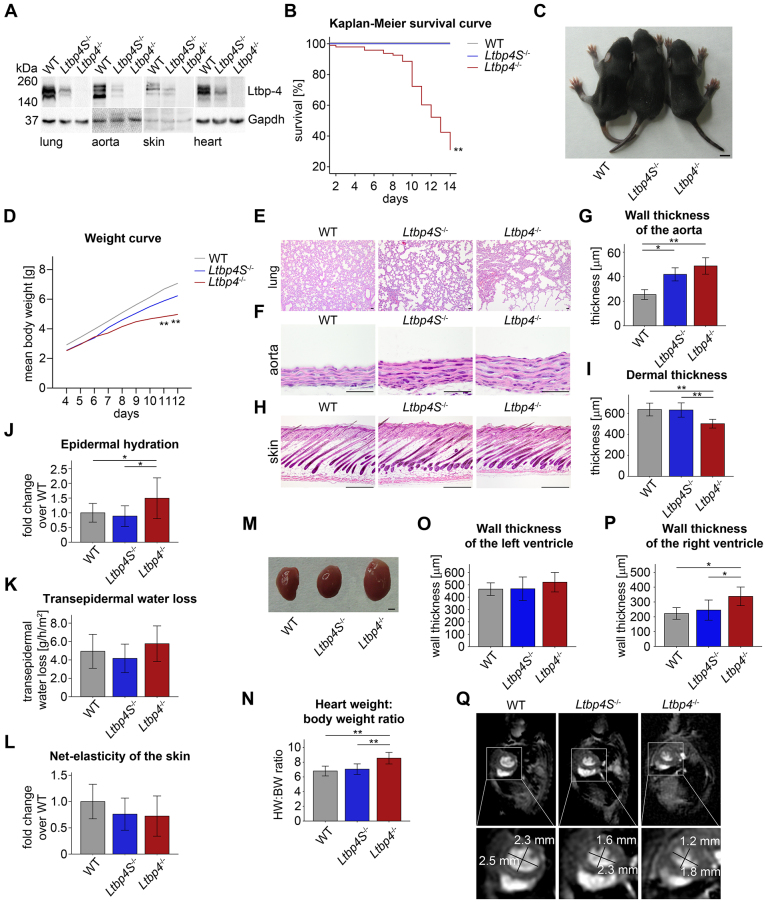
Fig. 1.
Clinical and morphological analyses of Ltbp-4 deficient mice. (A) Representative immunoblots of lung, aorta, skin and hearts showing the reduced or absent expression of Ltbp-4 in Ltbp4S−/− and Ltbp4−/− mice compared to WT mice. (B) Kaplan–Meier survival curve revealing the significantly higher neonatal mortality in Ltbp4−/− mice compared to Ltbp4S−/− and WT mice (n≥23; **P<0.01 versus WT). (C) Ltbp4−/− mice showed reduced body size compared to Ltbp4S−/− and WT mice. Scale bar: 0.5 cm. (D) The P4-P12 weight curve showed significantly reduced body weight of Ltbp4−/− mice compared to Ltbp4S−/− and WT mice (n≥8; **P<0.01 versus WT). (E) In Ltbp4S−/− mice, the pulmonary parenchyma showed enlarged alveolar spaces with reduced numbers of alveoli and multifocal areas of atelectasis compared to WT mice. Ltbp4−/− lungs revealed lack of lobular architecture, severely enlarged alveolar spaces and emphysematous areas compared to WT mice. Scale bars: 40 μm. (F,G) Aortas showed marked thickening of the aortic wall in Ltbp4S−/− and Ltbp4−/− mice compared to WT mice (n≥3; *P<0.05, **P<0.01). Scale bars: 40 μm. (H,I) Ltbp4−/− mice showed reduced dermal thickness compared to Ltbp4S−/− and WT mice (n≥5;**P<0.01). Scale bars: 200 μm. (J) The epidermal hydration was increased in Ltbp4−/− mice compared to Ltbp4S−/− and WT mice (n≥9; *P<0.05). (K) The transepidermal water loss tended to be higher in Ltbp4−/− mice compared to Ltbp4S−/− and WT mice (n≥9; not significant). (L) The net-elasticity of the skin of both Ltbp-4-deficient mice tended to be lower compared to WT mice (n≥9; not significant). (M) Representative images showing the increased size of hearts of Ltbp4−/− mice compared to hearts of WT and Ltbp4S−/− mice. Scale bar: 0.1 cm. (N) Heart weight:body weight ratios showing that hearts of Ltbp4−/− mice were significantly heavier than hearts of WT and Ltbp4S−/− mice (n≥7; **P<0.01). (O) Wall thickness of the left ventricle was not changed in Ltbp4S−/− and Ltbp4−/− mice compared to WT mice (n≥6; not significant). (P) Wall thickness of the right ventricle was significantly increased in Ltbp4−/− mice compared to Ltbp4S−/− and WT mice (n≥6; *P<0.05). (Q) Representative short-axis images from MRI analysis revealing a flattened interventricular septum resulting in a more oval shape of the left ventricle in Ltbp4S−/− and Ltbp4−/− mice compared to WT mice.