Figure 1.
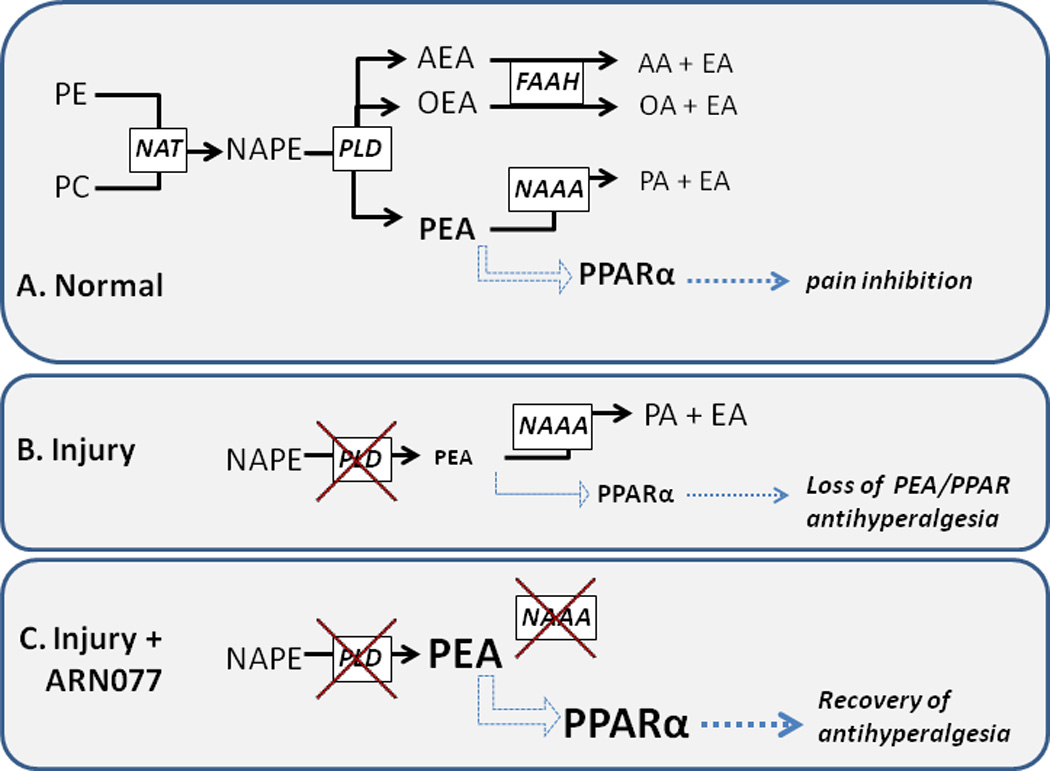
Proposed mechanism of pain inhibition by N-acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA). Panel A: key enzymatic pathways for fatty acid ethanolamide synthesis and degradation (solid black arrows), and a proposed mechanism of pain inhibition involving palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) activation of PPARα (blue arrows), and PPARα-mediated pain inhibition (green arrows). Panel B: Injury-induced inhibition of the enzyme that synthesizes PEA (N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D, NAPE-PLD) and ensuing loss of PEA-PPARα antihyperalgesia. Panel C: Inhibition of N-acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA) with the novel compound ARN077 raises PEA concentrations, thus reinstating PPARα antihyperalgesia.
PE, phosphatidylethanolamine. PC, phosphatidylcholine. NAT, N-acetyltransferase. NAPE, N-acylphosphatidylethanolamines. AEA, arachidonoylethanolamide (anandamide). OEA, oleoylethanolamide. AA, arachidonic acid. OA, oleic acid. PA, palmitic acid. EA, ethanolamine.
