Figure 3.
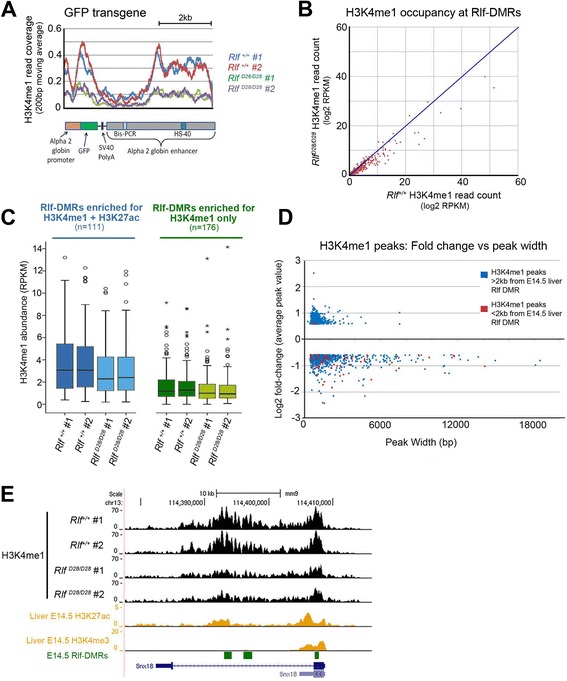
Rlf homozygous mutants show altered H3K4me1 occupancy across the genome. (A) H3K4me1 occupancy at the GFP transgene in chromatin extracted E14.5 fetal livers of two Rlf +/+ and two Rlf MommeD28/MommeD28 mice. (B) Scatter plot showing H3K4me1 occupancy at E14.5 liver Rlf-DMRs (C) A box-whisker plot showing H3K4me1 abundance in Rlf +/+ and Rlf MommeD28/MommeD28 mice at loci overlapping either putative active or poised regulatory regions in the E14.5 liver (marked by H3K4me1 and H3K27ac or H3K4me1 only, respectively). In both cases RPKM values for the homozygous replicates are significantly different from the wild-type replicates (Mann–Whitney U test: p < 1×10−8). (D) Scatter plot showing fold change of peaks with >50% alteration in H3K4me1 occupancy. Red and blue dots represent peaks either within 2 kb of a Rlf-DMR or further from a Rlf-DMR, respectively. (E) Screen shot showing a representative region with reduced H3K4me1 occupancy in Rlf MommeD28/MommeD28 mutants samples compared to Rlf +/+ mice. The position of three E14.5 liver Rlf-DMRs are represented by green boxes.
