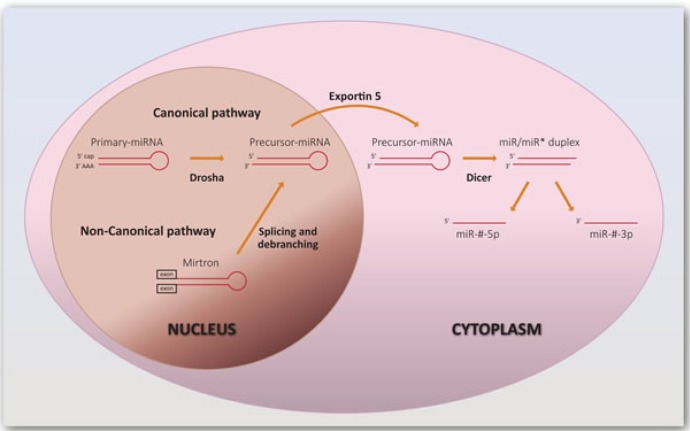
Figure 1. Biogenesis of miRNAs.
The synthesis of miRNAs via the canonical pathway starts with transcription of miRNA genes by RNA polymerase II, which results in primary-miRNAs. These are processed by Drosha and DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (DGCR8), generating precursor-miRNAs which are transported to the cytoplasm by Exportin 5 and cleaved by Dicer and TAR RNA-binding protein (TRBP). The resulting duplex is separated, generating mature miRNAs. MiRNAs can also arise from splicing through the non-canonical pathway. The designation of miRNAs includes the term “miR” preceding a number attributed sequentially. Similar sequences can have the same number but a different suffix (number or letter). Letters defining the species are added as prefixes, such as hsa for Homo sapiens. Additionally, they can be designated miR-#-3p or miR-#-5p depending on which arm of the precursor structure the leading strand is located [168].