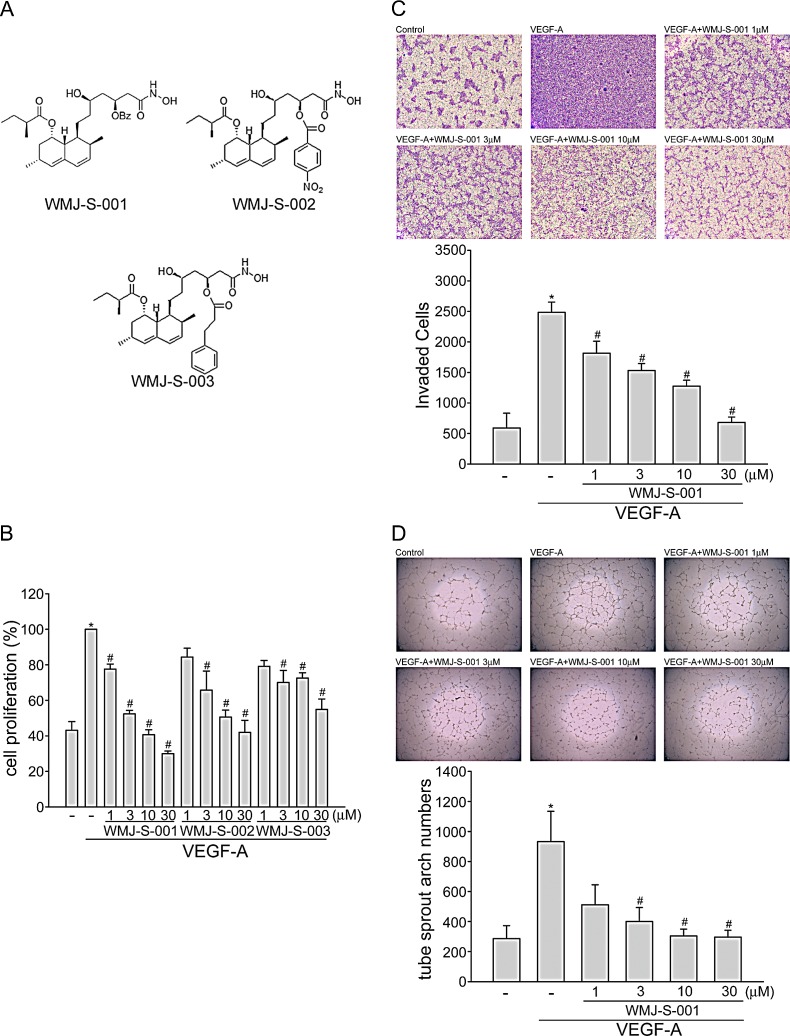
Fig.1. WMJ-S-001 inhibited VEGF-A-induced cell proliferation, invasion and tube formation.
(A) Chemical structures of WMJ-S-001, WMJ-S-002 and WMJ-S-003 (B) HUVECs were starved in 2 % FBS containing medium without ECGS for 16 h. After starvation, cells were pretreated with indicated concentrations of WMJ-S-001, WMJ-S-002 or WMJ-S-003 followed by the stimulation with VEGF-A (20 ng/ml) for another 24 h. Cell proliferation was determined as described in the Materials and Methods section. Each column represents the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05, compared with the group treated with VEGF alone. (C) After starvation as described in (B), cells were then seeded in the top chamber in the absence or presence of WMJ-S-001 at indicated concentrations using VEGF-A as chemo-attractant. After 16 h, invaded cells through the gelatin-coated membrane were stained and quantified. Each column represents the mean ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments. *p < 0.05, compared with the group treated with VEGF-A alone. (D) HUVECs were seeded on Matrigel in the presence of VEGF-A (20 ng/ml) with or without WMJ-S-001 at indicated concentrations. Cells were then photographed under phase-contrast after 16 h. Bar graphs show compiled data of average sprout arch numbers (n=4). *p < 0.05, compared with the group treated with VEGF-A alone.