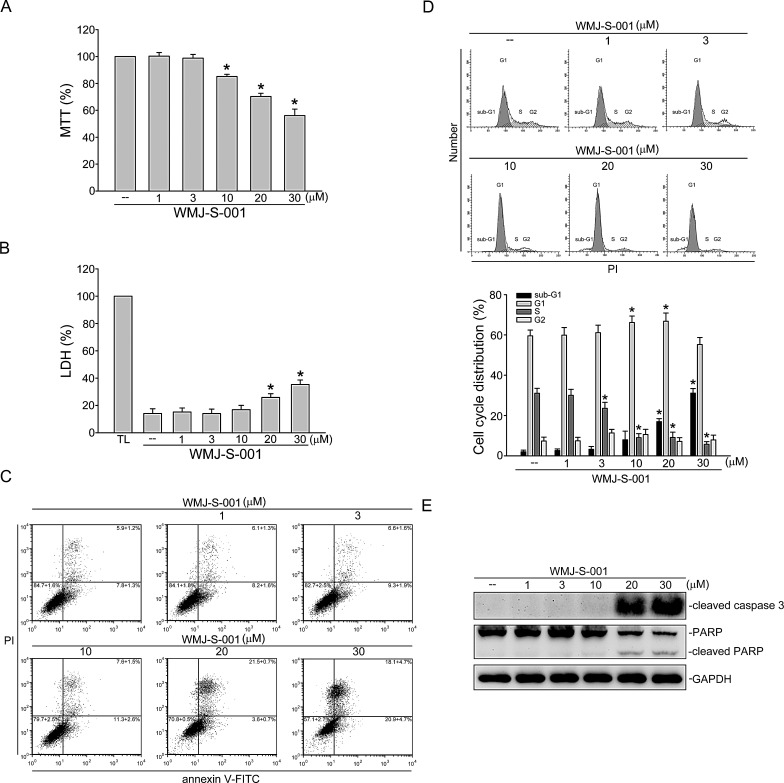
Fig.5. WMJ-S-001 affected cell cycle distribution and induced apoptosis in HUVECs.
(A) HUVECs were treated with indicated concentrations of WMJ-S-001 for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Each column represents the mean ± S.E.M. of five independent experiments performed in triplicate (*p < 0.05, compared with the control group). (B) HUVECs were treated with indicated concentrations of WMJ-S-001 for 24 h. The cytotoxicity of WMJ-S-001 was determined by LDH assay. Cells were also treated with cell lysis buffer (total lysis, TL) to serve as positive control. Each column represents the mean ± S.E.M. of five independent experiments performed in triplicate (*p < 0.05, compared with the control group). (C) Cells were treated with vehicle or WMJ-S-001 at indicated concentrations for 24 h. Cells were then stained with annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) for 15 min. The percentage of apoptotic cells was then analyzed by flow-cytometric analysis. Results shown are representative of four independent experiments. (D) Cells were treated as in (C), the percentage of cells in subG1, G0/G1, S, and G2/M phases was then analyzed by flow-cytometric analysis. Each column represents the mean ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments * p < 0.05, compared with the control group (E) Cells were treated as in (C), the extent of cleavage caspase 3and PARP were then determined by immunoblotting. Results shown are representative of four independent experiments.