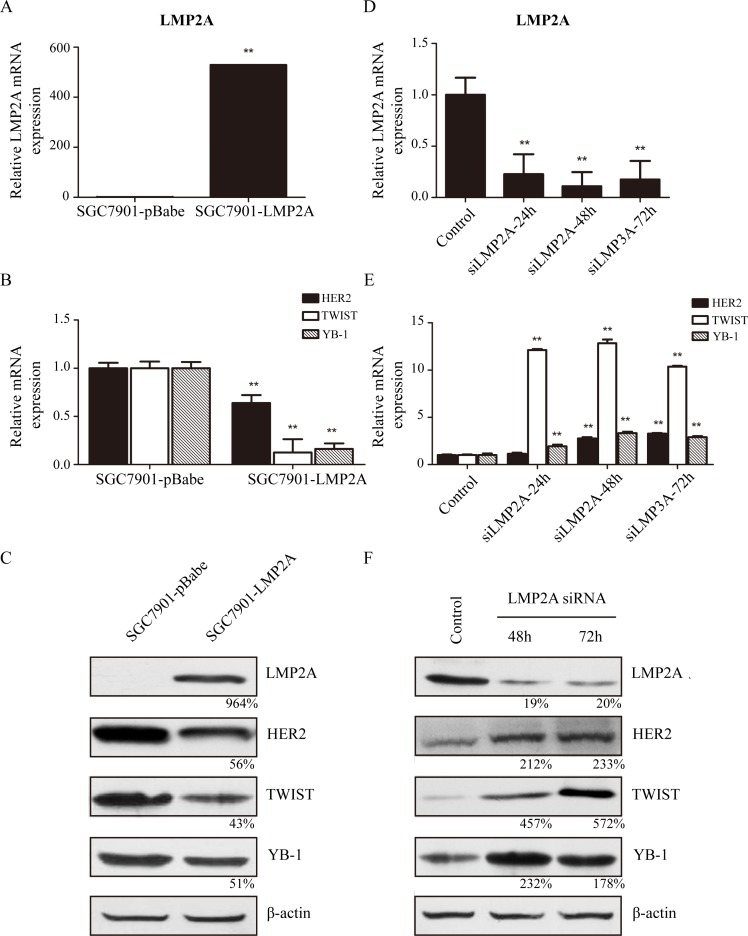
Figure 2. LMP2A inhibited expression of HER2, TWIST and YB-1 on both transcriptional and translational levels.
SGC7901 cells were stably nucleofected with an empty pBabe vector or vector subcloned with LMP2A. (A) qRT-PCR suggested that level of LMP2A mRNA was up-regulated in five hundred fold in SGC7901-LMP2A cells (**p<0.001 vs SGC7901-pBabe cells). (B) Following LMP2A mRNA levels increased, the mRNA levels of HER2, TWIST and YB-1 were significantly decreased (**p<0.001 vs SGC7901-pBabe cells). (C) Western blot analysis shows that the protein levels of HER2, TWIST and YB-1 were also reduced after LMP2A was exogenous overexpressed in SGC7901-LMP2A cells relative to SGC7901-pBabe cells. SNU719 cells were transiently nucleofected with LMP2A siRNA or a universal siRNA control for 24, 48 and 72 h. (D) qRT-PCR showed that the mRNA level of LMP2A in SNU719 siLMP2A cells was down-regulated after interfering 24h, and reduced by 89.1% at 48h (**p<0.001 vs control SNU719 cells). (E) When LMP2A mRNA levels decreased, mRNA levels of TWIST and YB-1 were significantly up-regulated by 12.84- and 3.32-fold at 48h, and HER2 mRNA increased by 3.28-fold at 72h (**p<0.001 vs control SNU719 cells). (F) Western blot analysis exhibited that the protein levels of HER2, TWIST and YB-1 were also increased after LMP2A was siRNA silenced in SNU719 siLMP2A cells relative to control SNU719 cells.