Figure 3. PIP3 increases phospho-PHBT258, phospho-IKKα/βS176/180, phospho-NF-kB p65S536 and COX-2 as well as formation of Ras/Raf/PHB/MEKK1/IKK complex in a phospho-Akt dependent manner.
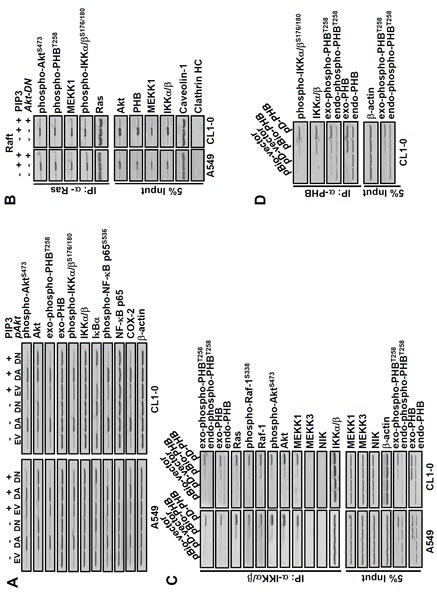
(A) dominant negative Akt (Akt-DN) attenuated the effects of PIP3 on not only COX-2 but also phosphorylation of Akt, PHB, IKKα/β and NF-kB. Lung cancer cells (A549 and CL1-0; 2 × 105/mL) transfected with empty vector (EV), dominant active-(DA) or dominant negative-(DN) Akt for 48 hours were treated with or without PIP3 (5 μM) for 24 hours as indicated. The protein levels were determined by immunoblotting. (B) lung cancer cells (2 × 105/mL) transfected with or without Akt-DN plasmid for 48 hours were treated with 5 μM PIP3 for 24 hours as indicated. The membrane raft fractions were immunoprecipitated with anti-Ras antibodies, and the immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Caveolin-1 and clathrin heavy chain (HC) protein served as membrane raft and non-raft markers, respectively. (C and D), cells were transfected with plasmids pBio-PHB, pD-PHB or empty vector (pBio-vector and pD-vector) for 48 hours, as indicated. The cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-IKKα/β or anti-PHB antibodies and the immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments.
