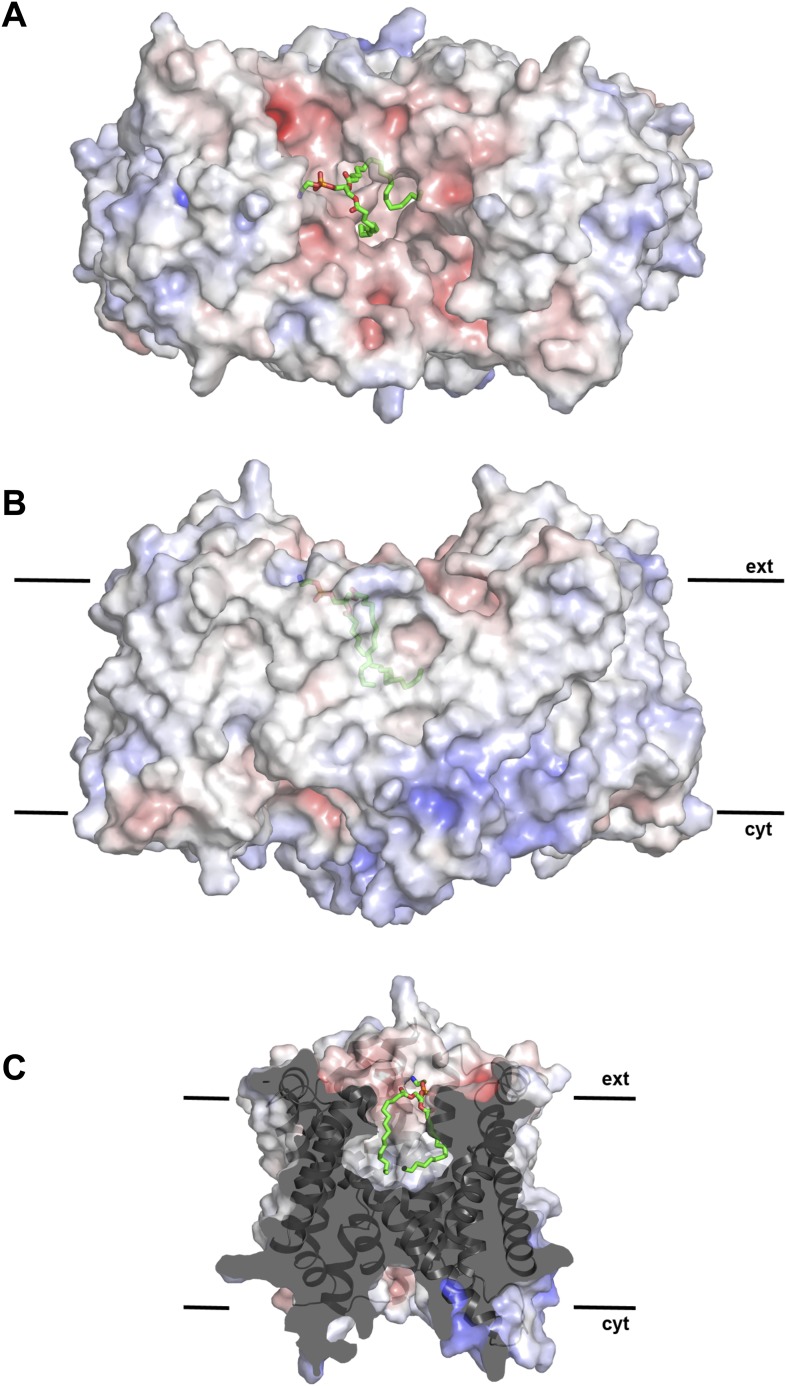
Figure 2. Hydrophobic extracellular cavity with bound lipid.
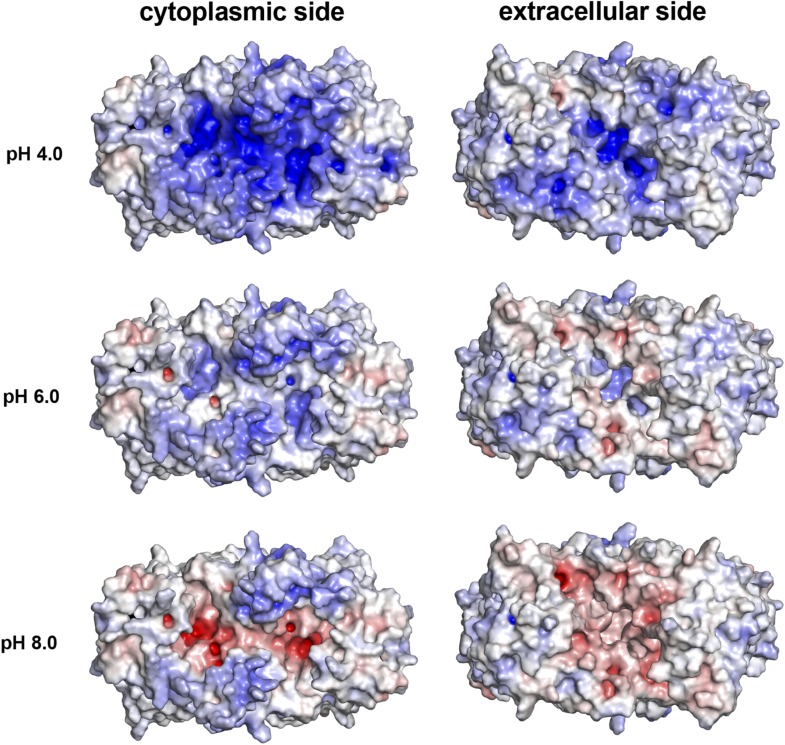
(A) One lipid molecule (PE, green) in the cavity between the two protomers in the dimer contributes to the hydrophobic contacts across the dimer interface. The extracellular surface is slightly negatively charged. (B) The alkyl chain of the lipid extends to the center of the molecule. (C) The lipid-facing surface of the central cavity is mainly hydrophobic. The surface potential was calculated at pH 7.0 by APBS.