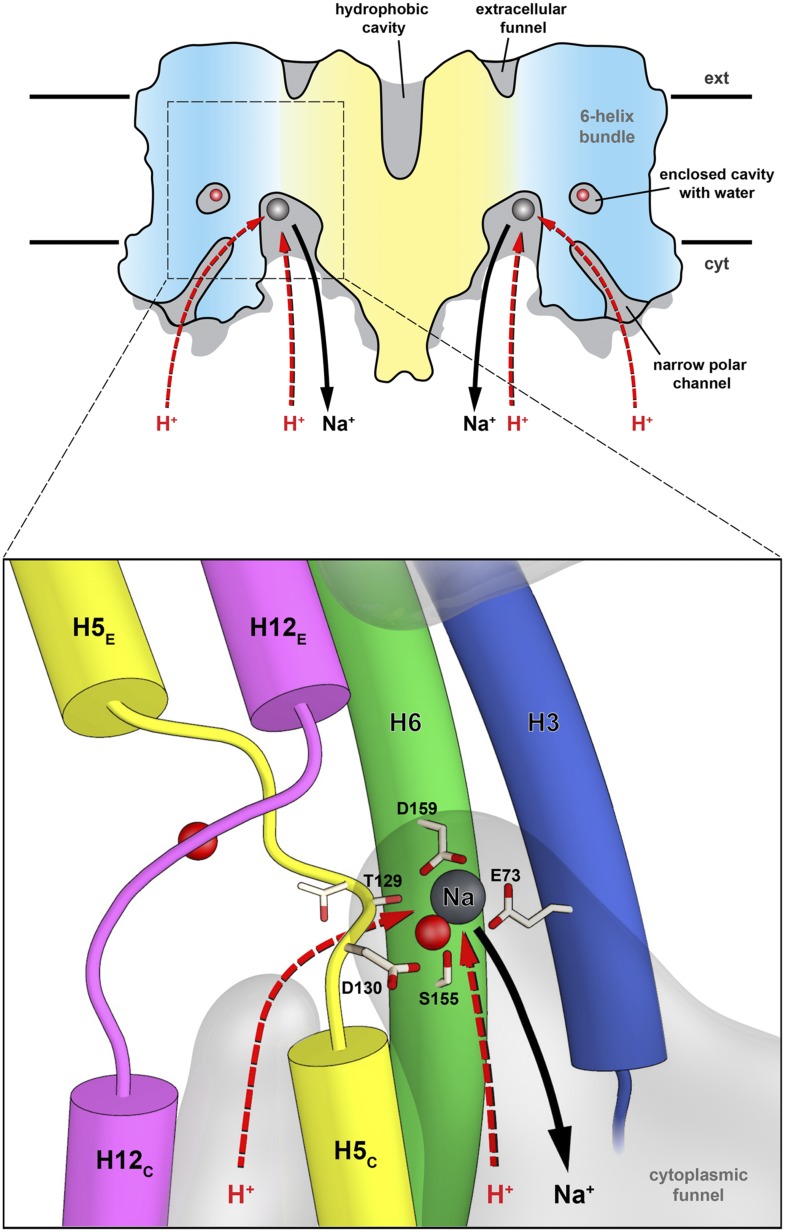
Figure 9. Substrate ion exchange on the cytoplasmic side.
The substrate-binding site of PaNhaP is located between the unwound stretches in the six-helix-bundle and the interface domain. The substrate ion is bound by acidic sidechains and polar groups in the bundle helices H5 and H6, and a glutamate in the interface helix H3 at the deepest point of the cytoplasmic funnel. While the funnel extends between the six-helix bundle and the dimer interface, the narrow polar channel is defined by the bundle helices H5C, H12C, H6 and H13. Protons may approach the binding site either through the cytoplasmic funnel, or through the narrow polar channel (red arrows). A proton displaces the bound substrate ion, which escapes to the cytoplasm (black arrow). Employing the narrow polar channel as the proton path would separate the Na+ ion and proton currents on the cytoplasmic side, which may be advantageous at high transport rates.