Figure 5.2.
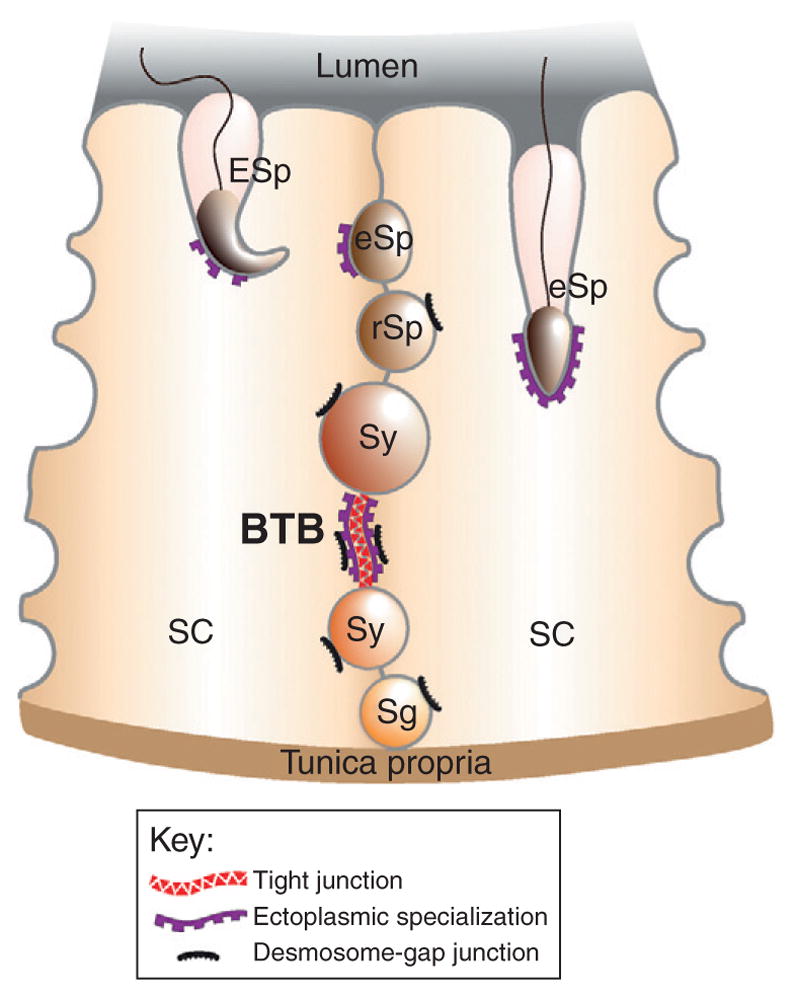
Sertoli–Sertoli and Sertoli–germ cell junctions. Two columnar Sertoli cells are shown sitting atop the tunica propria in the seminiferous epithelium. The BTB is constituted by adjacent Sertoli cells and composed of coexisting tight junctions, basal ectoplasmic specialization, and desmosome–gap junctions. Desmosome–gap junctions are found between Sertoli cells and all germ cells up to, but not including, step 8 spermatids, whereas the apical ectoplasmic specialization is found between Sertoli cells and all step 8–19 spermatids. Gap junctions and hemidesmosomes (a type of cell–matrix junction) are not illustrated since these junction types were not discussed in great detail. Also, it is also worth noting that two different stages of the seminiferous epithelial cycle are shown within a single panel (i.e., left, stage VII; right, stage VI) for the sake of simplicity, but this does not accurately represent the in vivo situation. Abbreviations: BTB, blood–testis barrier; SC, Sertoli cell; Sg, spermatogonium; Sy, spermatocyte; rSp, round spermatid; eSp, elongating spermatid; ESp, elongated spermatid.
