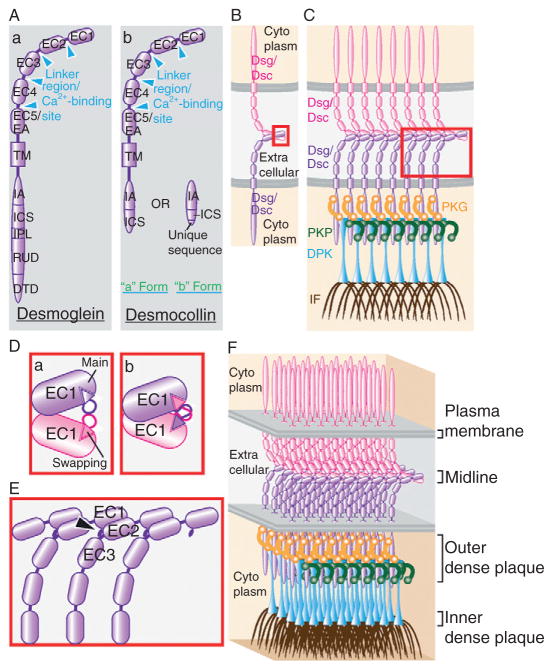
Figure 5.3.
Domain structure of desmosomal cadherins and the structure of desmosomes. (A) Different domains in desmosomal cadherins. From the N-terminus, desmogleins (a) and desmocollins (b) are composed of the following domains: extracellular (extracellular cadherin repeat, EC 1–5; connected by linker regions which contain Ca2+-binding sites), transmembrane (TM), and cytoplasmic (intracellular anchor (IA), intracellular cadherin-like sequence (ICS), intracellular proline-rich linker (IPL), repeat unit domain (RUD), desmoglein terminal domain (DTD)). Desmocollins do not contain IPL, RUD, and DTD, and the shorter “b form” has a truncated ICS followed by a unique sequence. It is worth noting that EC5 is sometimes known as the extracellular anchor (EA). (B) Trans-interaction of desmogleins (Dsg) or desmocollins (Dsc) between two opposing membranes. The boxed area represents the site of adhesion and is magnified in (D). (C) Organization of desmosomal cadherins (Dsg/Dsc), cytoplasmic plaque proteins and intermediate filaments (IF) at a desmosome. Plakoglobin (PKG) links desmosomal cadherins to desmoplakin (DPK), while plakophilins (PKP) link individual DPK molecules together laterally, which in turn tethers the desmosomal plaque to intermediate filaments. Boxed area is magnified in (E). (D) Strand-swap mechanism of cadherin adhesion. This diagram shows the EC1 domains of two trans-interacting cadherins (see B), before (a) and after (b) they undergo symmetrical strand swapping. Each molecule inserts its “swap domain,” also known as A strand, into the “main domain” of its partner. (E) Mechanism of Ca2+ independence. Within the compact arrangement in desmosomes (see C), the Ca2+-binding site between EC2 and 3 on each molecule is protected by a small β-strand in EC1 of the neighboring molecule (arrowhead). This results in the entrapment of bound Ca2+, even in low Ca2+ medium. (F) Compact arrangement within a desmosome. This dense arrangement of proteins leads to a few desmosomal-specific features discernable under the electron microscope. The midline in the extracellular space consists of the ends of desmosomal cadherin where the EC1 domains engage with each other. The outer dense plaque includes desmosomal cadherin cytoplasmic tails, plakoglobin, plakophilins, and the plakin domain of desmoplakin. The inner dense plaque is made up of the plakin repeat domains (PRD) of desmoplakin. The area in between outer and inner dense plaques consists of the rod domain of desmoplakin.