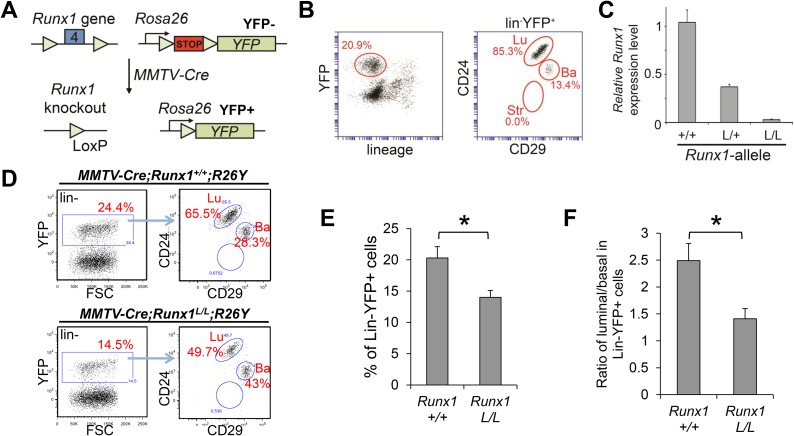
Figure 3. Runx1-loss leads to a reduction in the luminal MEC population.
(A) Schematic representation of the Runx1 conditional knockout allele in which its exon 4 is flanked by loxP sites, as well as the R26Y conditional Cre-reporter. STOP: transcriptional stopper cassette. Subsequent breeding with MMTV-Cre resulted in mice in which selected subsets of MECs express YFP and lack expression of functional RUNX1. (B) FACS gating strategy for detecting lin−YFP+ (lin: lineage markers) MECs, as well as YFP+ lin−CD24+CD29lo luminal (Lu), and lin−CD24+CD29hi basal (Ba) MECs in MMTV-Cre;R26Y females. Str: stromal cells. (C) qRT-PCR analysis confirming the loss of Runx1 expression in YFP+ MECs sorted from MMTV-Cre;Runx1L/L;R26Y females (L/L). (D) FACS analysis showing the reduced lin−YFP+ MEC population (left plots), as well as the reduced lin−YFP+ luminal population (right plots), in MMTV-Cre;Runx1L/L;R26Y female compared to those in MMTV-Cre;Runx1+/+;R26Y control female. (E–F) The percentages of lin−YFP+ MEC population (E), as well as the ratios of luminal/basal subpopulations among the lin−YFP+ gate (F), are significantly reduced in MMTV-Cre;Runx1L/L;R26Y females (n = 9) (L/L) compared to those in MMTV-Cre;Runx1+/+;R26Y control females (n = 10) (+/+). p values: *: p ≤ 0.05; error bars represent mean ± S.E.M.