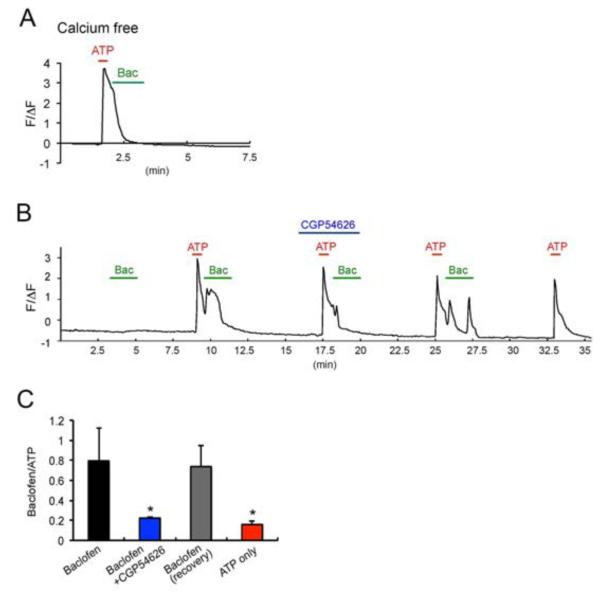
Fig. 3.
Baclofen-induced Ca2+ waves are ATP and extracellular calcium dependent. A. Representative trace of long-term imaging of baclofen-induced Ca2+ fluorescence changes (ΔF/F0). Data points are averages of 13 cells in the imaging field in one experiment. The horizontal bar represents the application of stimuli. Green: 100 μM baclofen, Red: 100 μM ATP, Blue: 1 μM CGP54626. B. Summary histograms showing that baclofen induces Ca2+ transients and it is reduced by pre-treatment with CGP54626 (blue). The second baclofen treatment (recovery, grey) after wash induced Ca2+ transient. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, compare to first ATP-baclofen stimulation (black) n=. C. Representative trace of baclofen-induced Ca2+ fluorescence changes (ΔF/F0) after removal of extracellular calcium. Data points are averages of 8 cells in the imaging field in one experiment. The horizontal bar represents the application of stimuli. Green: 100 μM baclofen, Red: 100 μM ATP.