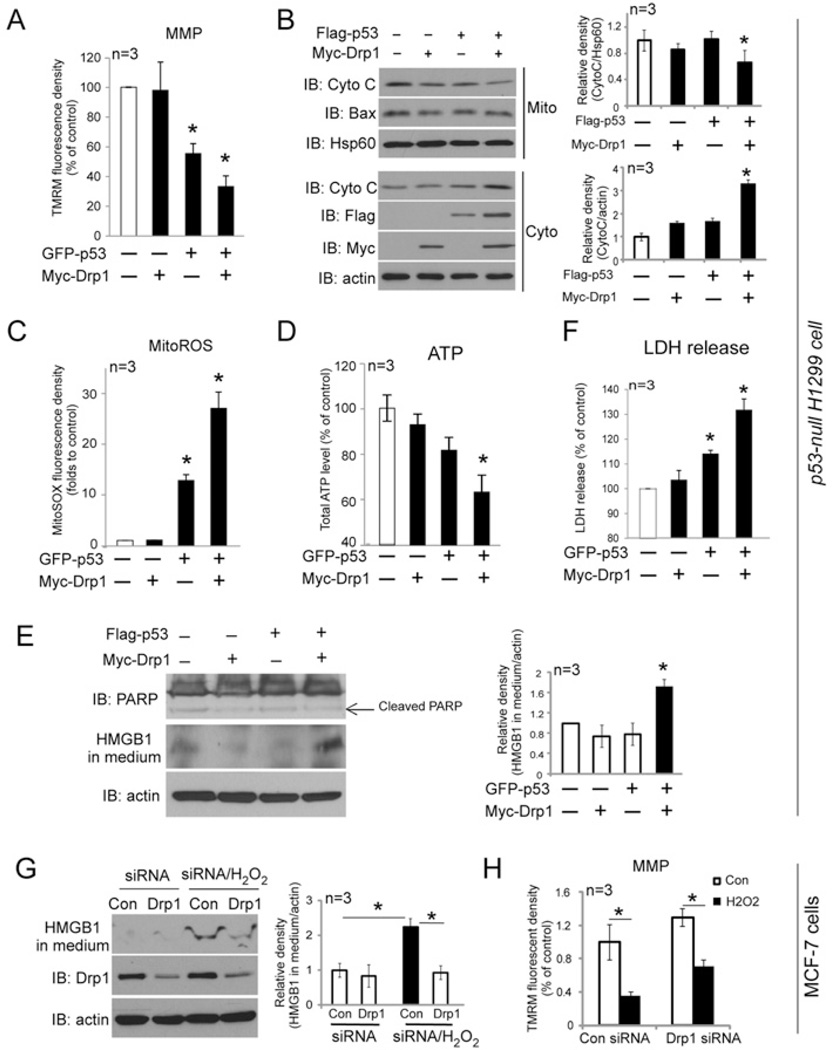
Figure 5. Drp1 and p53 interdependently induce mitochondrial damage and trigger necrosis.
(A, C, D and F) p53-null H1299 cells were co-expressed with GFP–p53 and/or Myc–Drp1. MMP, mitoROS production, total ATP levels and LDH release were determined. *P< 0.05 compared with control group. (B) H1299 cells were expressed with FLAG–p53 and/or Myc–Drp1. At 24 h after transfection, Bax and cytochrome c were examined in mitochondrial (Mito) and cytosolic (Cyto) fractions by immunoblotting. VDAC was used as a loading control for mitochondrial fractions. The protein levels of Bax and cytochrome c(Cyto C) were quantified. *P< 0.05 compared with control group. (E) H1299 cells were expressed with FLAG–p53 and/or Myc–Drp1. At 24 h after transfection, PARP cleavage and HMGB1 release were determined by immunoblotting. Actin was used as a loading control. The level of HMGB1 was quantified. *P< 0.05 compared with control group. MCF7 cells were transfected with control or Drp1 siRNA. After 36 h of transfection, cells were treated with H2O2 (600 µM) for 12 h. (G) Quantification of HMGB1 release in medium. (H) MMP was determined. *P< 0.05. Results in all histograms are means ± S.D. for three independent experiments. Con, control; IB, immunoblot.