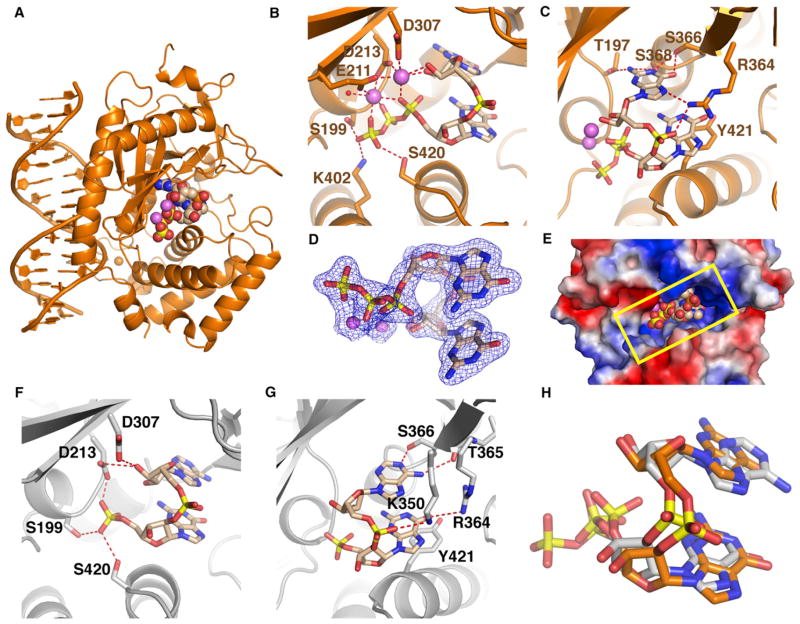
Figure 3. Structure of the Ternary Complex of cGAS and dsDNA with Bound 5′-pppG(2′,5′)pG and 5′-pG(2′,5′)pA.
(A) 1.9 Å crystal structure of the ternary complex of cGAS bound to dsDNA and 5′-pppG(2′,5′)pG. The protein and DNA are colored in orange in the ternary complex, with bound 5′-pppG(2′,5′)pG in a space-filling representation.
(B and C) Two alternate views of intermolecular contacts between 5′-pppG(2′,5′)pG and catalytic pocket residues in the ternary complex. Two cations are shown as magenta spheres, with hydrogen bonds shown by dashed red lines.
(D) 2Fo-Fc electron density map contoured at 1.2σ (blue) of bound 5′-pppG(2′,5′)pG in the catalytic pocket of the ternary complex.
(E) View of bound 5′-pppG(2′,5′)pG in a space-filling representation within the catalytic pocket, with the protein in an electrostatic representation.
(F and G) Two alternate views of intermolecular contacts between 5′-pG(2′,5′)pA and catalytic pocket residues in the 2.3 Å ternary complex of cGAS, dsDNA, and GMP + ATP.
(H) Superposition of structures of bound 5′-pppG(2′,5′)pG (orange) and 5′-pG(2′,5′)pA (silver).
See also Figure S3 and Tables S2 and S3.