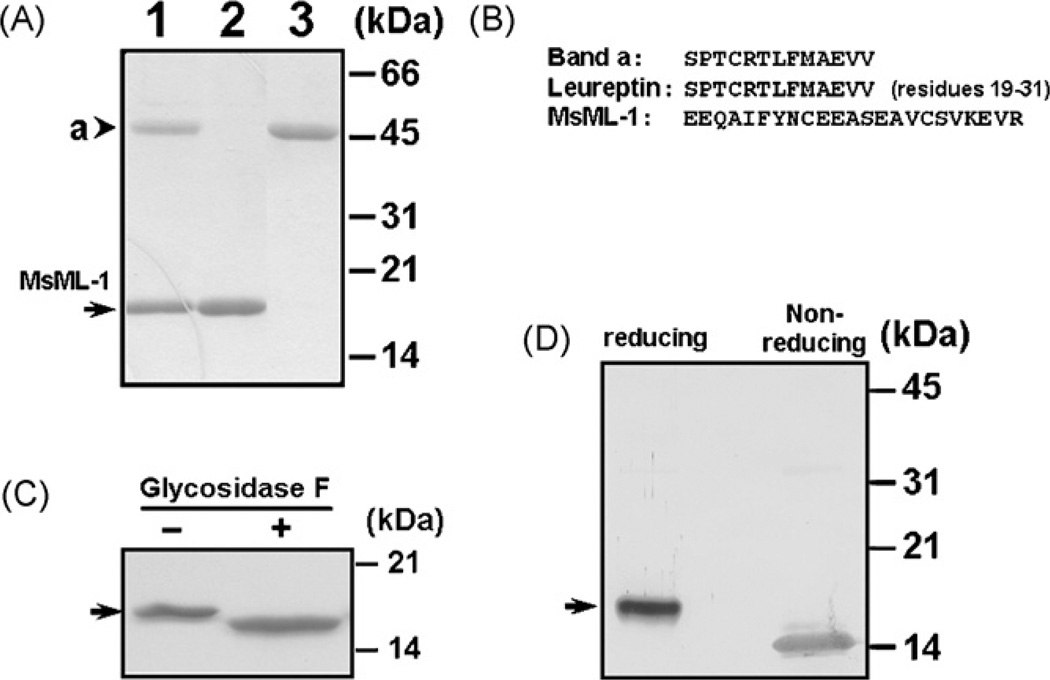
Fig. 1.
Analysis of M. sexta ML-1 (MsML-1) protein purified from hemolymph. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of MsML-1 purified from hemolymph. MsML-1 and a 46-kDa protein were purified to homogeneity from hemolymph after several chromatographies. Co-purified MsML-1 and the 46-kDa protein (lane 1, 3µg) and purified MsML-1 (lane 2, 2µg) and the 46-kDa protein (lane 3, 2µg) were analyzed by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the gel was stained by Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (B) Amino-terminal sequences of MsML-1 and the 46-kDa protein. The amino-terminal sequences of MsML-1 and the 46-kDa protein (band a) were determined by Edman degradation, and the sequence of leureptin (residues 19–31) was obtained from the Genbank database (accession number: AAO21503). (C) Deglycosylation of MsML-1. MsML-1 (2.0µg) purified from hemolymph was heated to 100 °C for 3 min in 20 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.2. The denatured protein was then incubated with or without 1U of N-glycosidase F (PNGase F) (Sigma) in 50µL of 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.2, 0.1% SDS, 0.5% (v/v) Nonidet P-40 and 0.5% (v/v) 2-mercaptoethanol for 24 h at 37 °C. Both N-glycosidase F treated and untreated MsML-1 samples (1.0µg each) were analyzed by 15% SDS-PAGE and the gel was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (D) Immunoblotting analysis of MsML-1 under reducing and non-reducing conditions. MsML-1 (0.5µg each) purified from hemolymph was dissolved in the sample loading buffer in the presence (reducing) or absence (non-reducing) of β -mercaptoethanol and heated to 95 °C for 5 min. Protein samples were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and MsML-1 was identified by immunoblotting using rabbit polyclonal antiserum against recombinant MsML-1. The arrowhead indicates the 46-kDa protein (band a) while the arrows indicate native MsML-1.