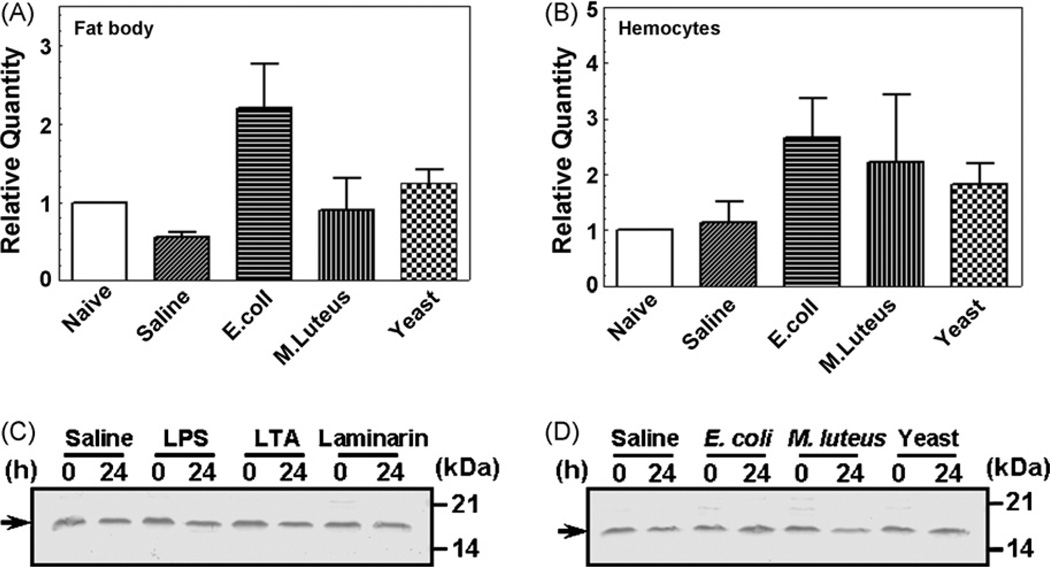
Fig. 4.
Expression of MsML-1 mRNA in fat body and hemocytes and MsML-1 protein in hemolymph after immune challenge. Day 2 fifth instar M. sexta larvae were injected with heat-killed E. coli (108 cells/larva), M. luteus (100µg/larva), yeast (S. cerevisiae) (107 cells/larva) or saline (as a control). Hemocytes and fat body were collected at 24 h post-injection. Total RNAs were prepared from these hemocytes and fat body, and then transcribed into cDNAs using GeneRacer™ Oligo-dT primer. Expression of MsML-1 mRNA in microbial challenged hemocytes or fat body was determined by real-time PCR in three replicas (A and B). The bars represent the mean of three individual measurements±S.E.M. For MsML-1 protein expression in hemolymph after immune challenge (C and D), day 2 fifth instar M. sexta larvae were injected with saline (as a control), heat-killed E. coli, M. luteus or yeast (S. cerevisiae) as described above, or with LPS (E. coli 026:B6), LTA or laminarin (20µg each per larva) (four larvae for each group). Hemolymph was collected from each larva at 0 and 24 h after injection and equal volumes of the plasma samples were mixed, diluted (1:1 in water), and then added to the 2 × SDS loading buffer. For electrophoresis, diluted plasma samples (each corresponding to 2 µL of the original mixed plasma) were loaded to 15% SDS-PAGE. MsML-1 in each plasma sample was detected by immunoblotting using rabbit polyclonal antibody to recombinant MsML-1. The arrows indicate MsML-1 protein in hemolymph.