FIG. 6.
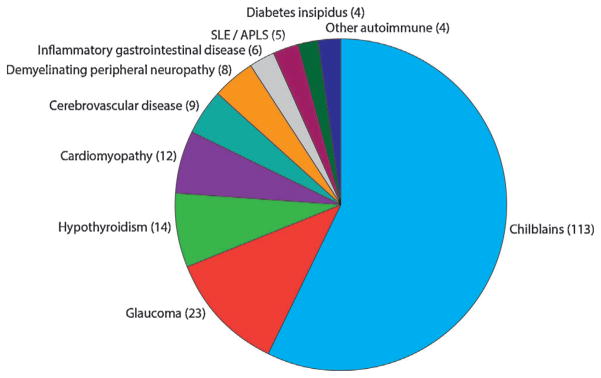
Frequency of associated phenotypes in AGS patients. Number of patients with either biallelic mutations or a recognized dominant mutation in one of the known AGS-related genes, in families where at least one individual has a neurological phenotype, i.e., excluding families with FCL only. SLE/APLS: Systemic lupus erythematosus/antiphospholipid syndrome. Inflammatory gastrointestinal disease: Crohns disease, atrophic gastritis, coeliac disease, autoimmune hepatitis, non-specific colitis. Other autoimmune: one diabetes mellitus, one hyperparathyroidism, one growth hormone deficiency, one adrenal insufficiency.
