Figure 6. STEVOR binding to RBC correlates with the level of GPC on the RBC surface.
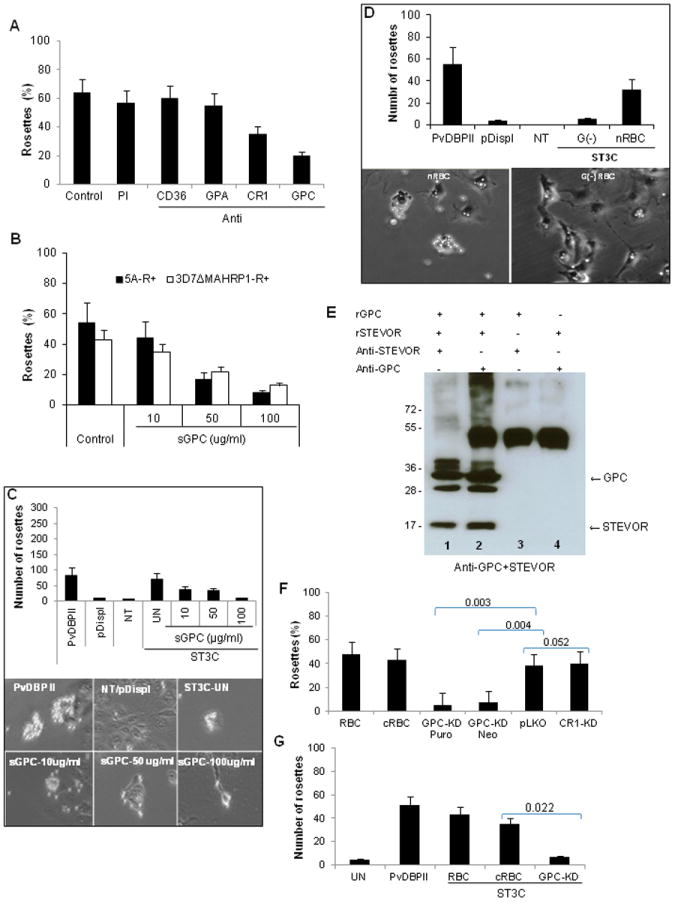
A- Effects of RBC treatment with 50 μg/ml of monoclonal antibodies against CD36, GPA, CR1 and GPC on rosette reformation of purified 5A-R+ iRBCs. Untreated RBCs (control) or RBCs treated with preimmune serum (PI) were used as controls. Data represent the average of two independent experiments. B and C- Concentration-dependent inhibition of rosetting of purified 5A-R+ and 3D7ΔMAHRP1-R+ iRBCs by soluble GPC (B) and binding of COS7 expressing ST3C construct (C). Soluble GPC reduces both the number of ST3C-expressing COS7 cells binding to RBC (C, top panel graph) as well the size of rosettes formed (C, bottom panel images) in a concentration-dependent manner compared to control (ST3C-UN). PvDBPII and untransfected (NT) and/or pDisplay vector-transfected (pDispl) were used as positive and negative controls for binding, respectively.D- Impairment (top panel graph) of binding of COS7 expressing ST3C to Gerbich negative (G(-)) RBC compared to normal RBC (nRBC) as illustrated by micrograph images (bottom panel images). PvDBPII and untransfected (NT) and/or pDisplay vector-transfected (pDispl) were used as positive and negative control for binding respectively. Data are presented as average of two independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. E- Pull down assay with recombinant STEVOR (rSTEVOR) and Glycophorin C (rGPC) in the presence (+) or absence (-) of anti-STEVOR or anti-GPC antibodies showing specific interactions of STEVOR and GPC (lanes 1 and 2). F and G- Impact of GPC knock down (KD) on rosetting of 5A-iRBCs (F) and ST3C binding (G). Rosetting was greatly reduced when performed with GPC knock down (KD) RBCs following puromycin (Puro, 97% KD compared to pLKO control, see also Figure S5) and Neomycin (Neo, 89% KD compared to pLKO control, Figure S5) selection compared to pLKO.In vitro generated-RBC (cRBC) and donor RBC (RBC) were used as controls. CR1 KD (27% KD compared to pLKO control, see also Figure S5) has no impact on rosetting. For ST3C binding (G), only Puromycin- selected GPC-knock down RBCs were used due to the limited number of available cells. Statistical differences of GPC and CR1-KD in comparison to pLKO control are shown.
Data represent the average of three independent experiments. Error bars denote standard deviation.
