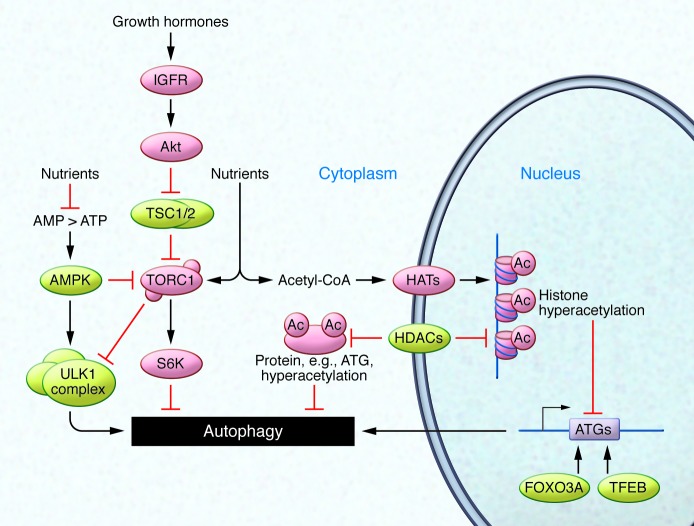
Figure 2. Nutrient and growth factor signaling regulates autophagy induction.
Growth factor binding to IGFR and/or nutrient availability stimulates the TORC1 pathway, which in turn deactivates the pro-autophagic ULK1 complex and activates the autophagy inhibitory kinase S6K. Cellular energy resources are also detected by AMPK, which initiates pro-autophagic signaling when the AMP/ATP ratio rises. Recent data have underscored the importance of post-translational protein acetylation (Ac), which is controlled by HATs such as EP300, HDACs such as SIRT1, and levels of acetyl-CoA. In addition to epigenetic regulation via histone acetylation and methylation, transcription factors such as FOXO3A or TFEB also influence transcription of pro-autophagic genes (e.g., ATGs).