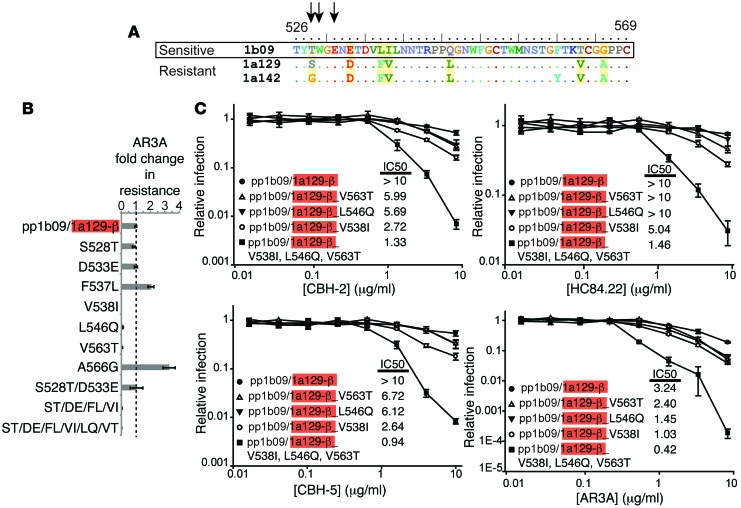
Figure 7. V538I/L546Q/V563T mutations in E2 confer additive sensitivity to NC1 mAbs.
(A) Alignment of amino acids 526–569 of sensitive E1E2 clone 1b09 and resistant clones 1a129 and 1a142. Homology to the 1b09 amino acid sequence is indicated by a dot. Positions that differ between the sensitive and both resistant clones are highlighted in yellow. Arrows indicate contact residues for AR3C in the E2 core/AR3C crystal structure. (B) The dashed line indicates relative infection of HCVpp with chimeric E1E2 1b09/1a129-β in the presence of the mab AR3A, adjusted to 1. Each subsequent bar indicates the fold change in neutralization resistance after the indicated mutation(s) were introduced. Error bars indicate SD between duplicate wells. (C) Neutralization by serial dilutions of the indicated mAb of HCVpp with chimeric E1E2 1b09/1a129-β (pp1b09/1a129-β) or pp1b09/1a129-β after introduction of the indicated mutation(s). Error bars indicate SD between duplicate wells.