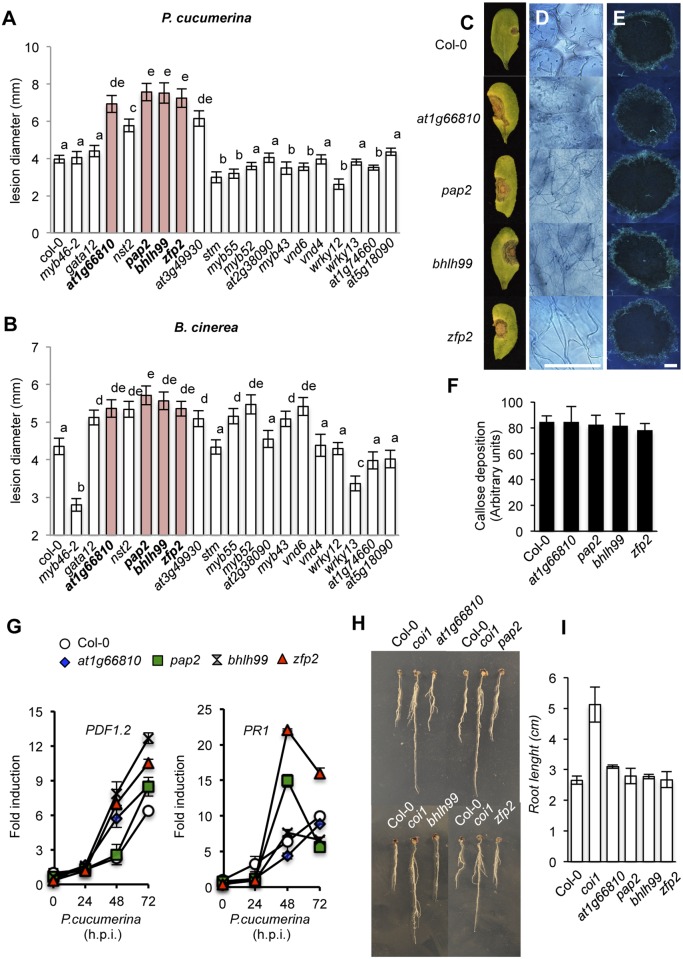
Fig 1. Characterization of disease resistance response of 18 mutants defective in the different transcription factors (TFs) identified as co-regulated with MYB46 and CESA4, CESA7 and CESA8.
(A-B) Resistance response to P. cucumerina (A) and B. cinerea (B) in Col-0 and TF mutant plants evaluated 10 d post inoculation by determining average lesion diameter on four leaves per plant and from 15 plants per genotype. Data points represent average lesion size ± SE of measurements. An ANOVA was conducted to assess significant differences in disease symptoms, with a priori P < 0.05 level of significance; the letters above the bars indicate different homogeneous groups with statistically significant differences. (C) Representative leaves from Col-0, zfp2, bhlh99, pap2, and at1g66810 plants at 10 d post inoculation with a 6-μL droplet of spores (2 x 104 conidia mL-1; as in A) of P. cucumerina. (D) Trypan blue staining, at 72 h postinoculation (h.p.i) with P. cucumerina, shows increased proliferation and growth of fungal hyphae in the four mutants when compared to Col-0. (E) Aniline blue staining and epifluorescence microscopy was applied to visualize callose accumulation. Micrographs showing callose deposition following P. cucumerina infection in Col-0 and the four mutant plants at 48 h.p.i. Scale bars represent 500 μm. (F) Pathogen-induced callose deposition was calculated as arbitrary units by quantifying the number of yellows pixels per million on digital micrographs of infected leaves at 48 hpi. Bars represent mean ± SD, n = 15 independent replicates. (G) PDF1.2 and PR-1 expression in Col-0 and in the disease susceptible mutants zfp2, bhlh99, pap2, and at1g66810 in early P. cucumerina infection stages. Relative expression was assayed over a 72-h time course by quantitative RT-PCR on total RNA from leaves following inoculation with a drop of spore suspension of P. cucumerina. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Expression was normalized to the constitutive ACT2 gene. (H-I) zfp2, bhlh99, pap2, and at1g66810 mutants, wild-type (Col-0) and coi1 sensitivity to JA. Seedlings were grown for 7 days on agar plates supplemented with 50 μM JA. Root length reduction, diagnostic of sensitivity to JA, revealed no differences between the TF mutants and Col-0. The coi1-40 mutant was insensitive to the hormone.