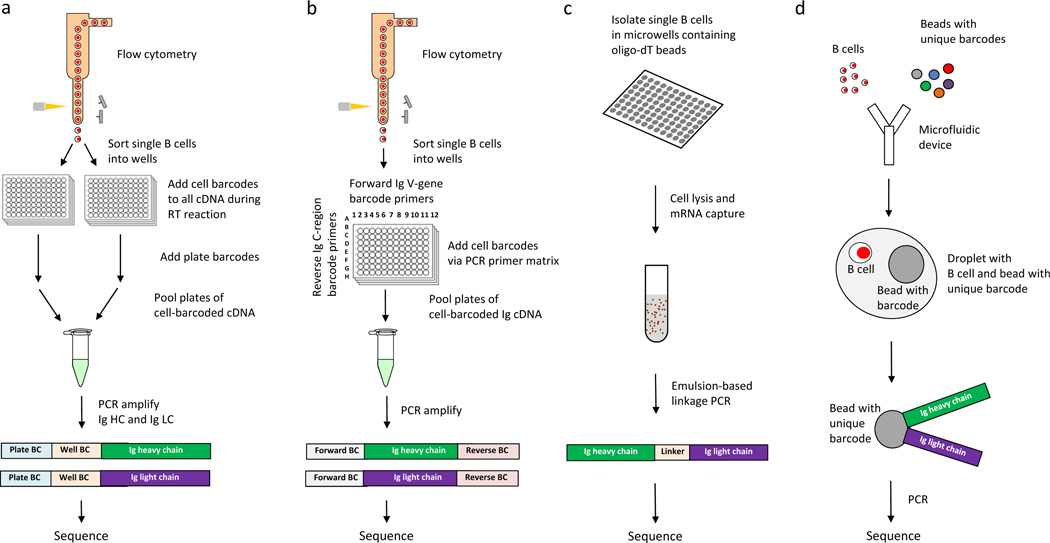
Figure 2.
Approaches for high-throughput sequencing of functional antibody repertoires. Comprehensive characterization of the functional antibody repertoire necessitates high-throughput, full-length and error-free sequencing of IgH and IgL pairs expressed by individual B cells. a | Cell barcoding via linkage PCR. Single B cells are isolated and lysed, then their RNA is captured by poly-T beads. cDNAs of the IgH and IgL expressed by individual B cells are then linked by emulsion to RT-PCR, and then pooled and sequenced.82 b | Cell barcoding via template switching. Single B cells are sorted, the template switching activity of RT adds a unique cell-specific barcode to all cDNAs generated from an individual B cell. Plate-specific barcodes are then added, resulting in cDNAs that have compound cell barcodes. Finally, the compound cell-barcoded IgH and IgL genes are amplified by PCR, pooled and sequenced.27,34,43 c | Cell barcoding by forward and reverse primer matrix. Single B cells are sorted, then V-gene forward primers and C-region reverse primers are used to add cell-specific barcodes to, and amplify by PCR, IgH and IgL cDNA generated from an individual B cell. Single-barcoded immunoglobulin genes are then pooled and sequenced.85 d | Microfluidic combination of beads with unique barcodes and single B cells into individual droplets. Using microfluidics, single B cells and beads with unique barcodes are combined in individual droplets, followed by lysis of the B cell, PCR and sequencing.61,83 Abbreviations: C, constant; IgH, immunoglobulin heavy chain; IgL, immunoglobulin light chain; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; RT, reverse transcriptase; V, variable.