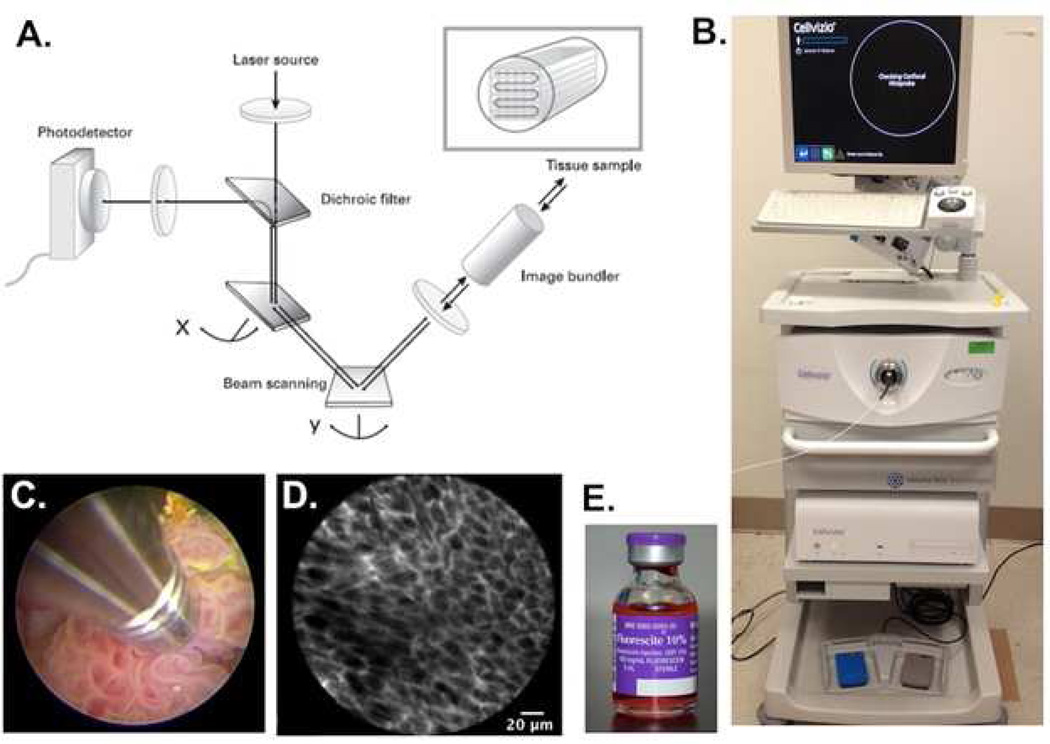
Fig. 1.
Mechanism and method of confocal laser endomicroscopy. A) Schematic representation of the technology underlying CLE. A laser beam is directed to the tissue sample via an image bundler. The resulting emission of light is retrieved and filtered through a pinhole before reaching the photodetector; B) Clinical grade CLE system (Cellvizio) from Mauna Kea Technologies. The workstation includes a laser scanning unit for probe attachment and a computer with software for image acquisition and processing. C) Direct probe contact of a papillary tumor for image acquisition. D) High-resolution image of subsurface cellular features acquired from CLE. The fluorescence signal is coming from the extracellular matrix stained by fluorescein. E) Fluorescein, an FDA-approved contrast agent, can be administered intravenously or topically for CLE imaging