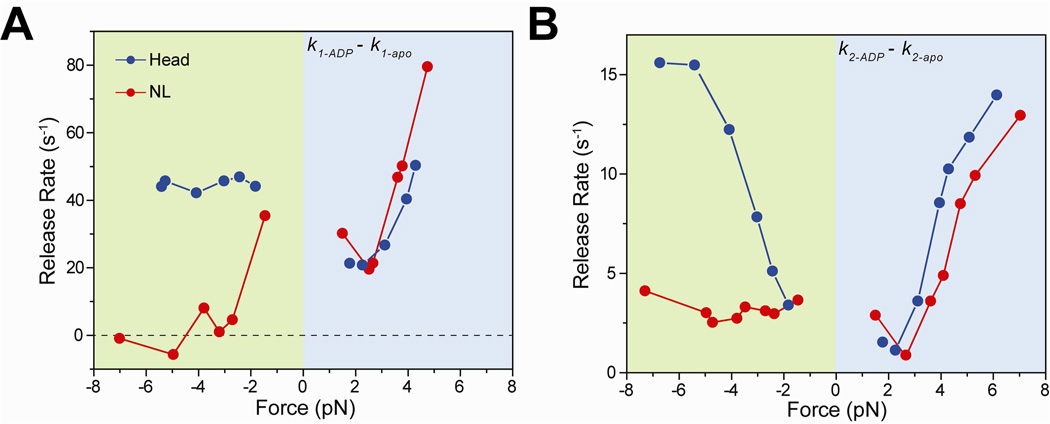
Figure 3. Nucleotide binding to a kinesin head is inhibited when the NL is oriented backward.
(A) k1 values of the apo condition were subtracted from that of 1 mM ADP to calculate the nucleotide-binding induced MT release rate from the weakly-bound state. k1-ADP − k1-apo of NL-pulled kinesins was 35 s−1 at −1.5 pN, and decreased to ~0 s−1 at higher negative forces. (B) k2 values of the apo condition were subtracted from that of 1 mM ADP to calculate the nucleotide-binding induced MT release rate from the strongly-bound state. k2-ADP − k2-apo of NL-pulled kinesins remained nearly constant at 3.0 s−1 under negative forces, whereas k2-ADP − k2-apo of head-pulled kinesins increased from 3.4 s−1 at −1.8 pN to 14.2 s−1 at −6.7 pN.