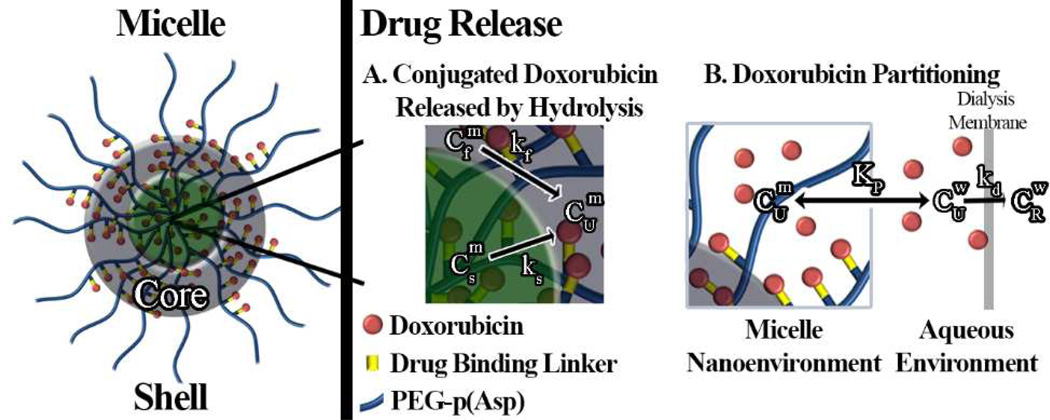
Figure 1.
Illustration of the mathematical model and parameters used to describe heterogeneous Dox release kinetics from three different micelle formulations (HYD-M, ABZ-M, and GLY-M). Here, the hydrophilic PEG shell surrounds a core consisting of two populations of conjugated Dox corresponding to fast ( ) and slow ( ) hydrolysis governed by rate constants k1 and k2, respectively. After hydrolysis, unconjugated Dox may partition into the micelle ( ) or reside in the aqueous environment ( ), as governed by the partition coefficient Kp. In dynamic dialysis studies, Dox transport though the dialysis membrane is governed by the rate constant kd and unbound Dox concentration,.