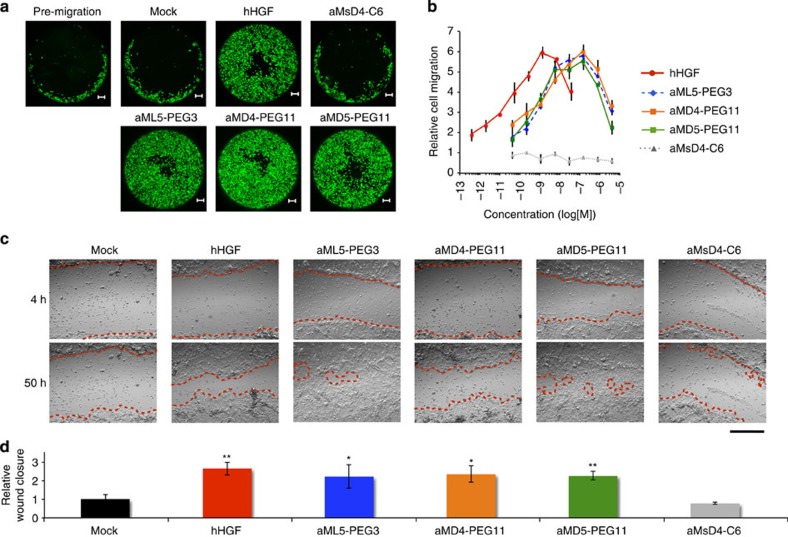
Figure 5. Cellular migration and wound healing promoted by dimeric macrocycles.
(a) Captured images for migration of normal human RPTEC stimulated by hHGF (0.26 nM) or dimer macrocycles (20 nM) over 30 h. Cells were stained by calcein-AM. Scale bar, 200 μm. (b) Dose-dependent titration of cell migration stimulated by 0.4 pM–30 nM of hHGF (red), 40 pM–3,000 nM of aML5-PEG3 (blue), aMD4-PEG11 (orange), aMsD4-C6 (grey) as a negative control, or aMD5-PEG11 (green). Migrated cells were stained with calcein-AM and quantified by fluorescence intensity. s.d. was calculated from the results of experiments in triplicate. (c) Captured images of wound healing in NHEK promoted by various stimulants (also see Supplementary Movie 1). Wound-closure events in the presence or the absence of 0.25 nM hHGF or 100 nM dimeric macrocycles were monitored by a real-time cultured cell monitoring system. The images were taken at 4 and 50 h. Red broken lines indicate boundaries between cells in the monolayer and the scratched areas uncovered by cells. Scale bar, 500 μm. (d) Quantification of relative wound-closure areas. Error bars denote s.e.m. (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (unpaired Student’s t-test) compared with Mock.