Figure 8.
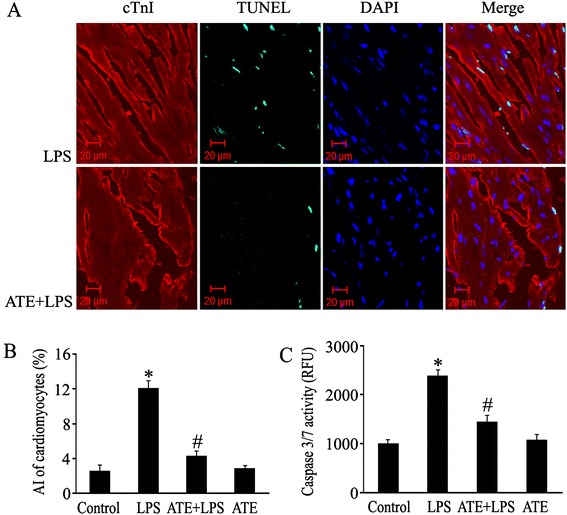
Atenolol (ATE) inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in lipolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged mice. Animals received intraperitoneal injection of normal saline or ATE (10 mg/kg) 1 hour before normal saline or 20 mg/kg LPS administration. At 12 hours after LPS administration, cardiomyocyte apoptosis was examined by TUNEL assay. (A) Representative photomicrographs of TUNEL assay (green) in the hearts from LPS and ATE plus LPS groups. Total nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue) and cardiomyocytes with anti-cTnI antibody (red). (B) Apoptotic index (AI) of cardiomyocytes (mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM); n = 8). (C) Cardiac caspase 3/7 activity at 6 hours after LPS administration (mean ± SEM; n = 8). * P <0.05 compared with the control group; # P <0.05 compared with the LPS group.
