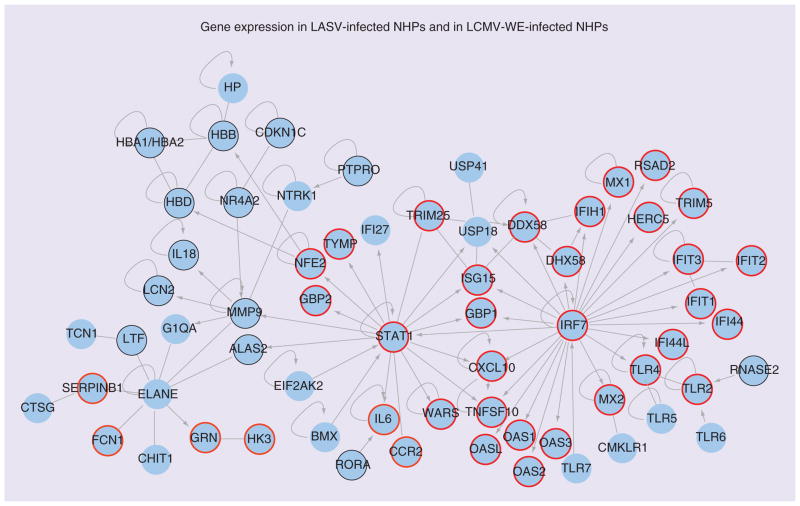
Figure 3. Genes differentially regulated in periperal blood mononuclear cells of Lassa virus-infected and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus WE strain-infected monkeys.
Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software was used to analyze a list of genes upregulated in periperal blood mononuclear cells after Lassa challenge of cynomolgus macaques. The blue circles contain symbolic gene names, the products of which participate in protein–protein interactions, straight lines represent simple interaction, arrows represent control of one gene product by another and loops represent self-regulation. Those genes encircled in red were also noted to be expressed in the LCMV-WE-infected nonhuman primate by [80]. It is notable that the gene products connected to the IRF7 node are similarly upregulated in Periperal blood mononuclear cells exposed to either virulent LCMV-WE or nonvirulent LCMV-ARM. In LCMV-WE-infected NHP, no effects were seen on ELANE, strong downregulation (encircled in black) was seen for NR4A2 and mild to insignificant downregulation of hemoglobins (HBA, HBB, HBD), CDKN1C, IL-18, MMP9, LCN2, LTF, ALAS2, RORA and RNASE2 was observed [80].
LASV: Lassa virus; LCMV-ARM: Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus Armstrong strain; LCMV-WE: Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus WE strain; NHP: Nonhuman primate.
Adapted with permission from Figure 3 of [126].