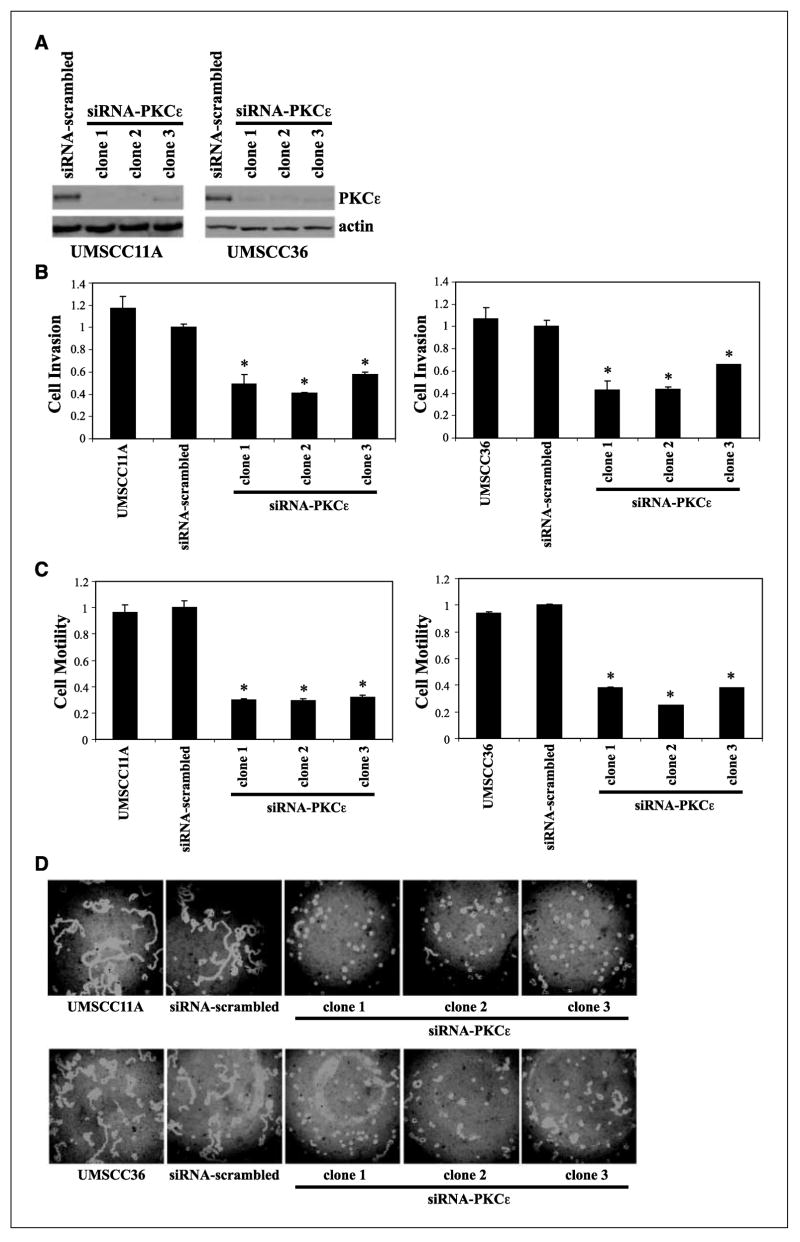
Figure 2.
RNAi-mediated disruption of PKCε inhibits invasion and motility in UMSCC11A and UMSCC36. A, siRNA-PKCε UMSCC11A and UMSCC36 clones have reduced PKCε protein levels. B, PKCε-deficient UMSCC11A and UMSCC36 clones are significantly less invasive than siRNA-scrambled control cells or untransfected parental cells. *, P < 0.006 for siRNA-PKCε UMSCC11A and P < 0.01 for siRNA-PKCε UMSCC36 compared with siRNA-scrambled control cells. C, PKCε-deficient UMSCC11A and UMSCC36 clones are significantly less motile than siRNA-scrambled control cells or untransfected parental cells. *, P < 0.0005 for siRNA-PKCε UMSCC11A and P < 0.0001 for siRNA-PKCε UMSCC36 compared with siRNA-scrambled control cells. D, representative cell motility field for each cell line and PKCε-deficient clone.