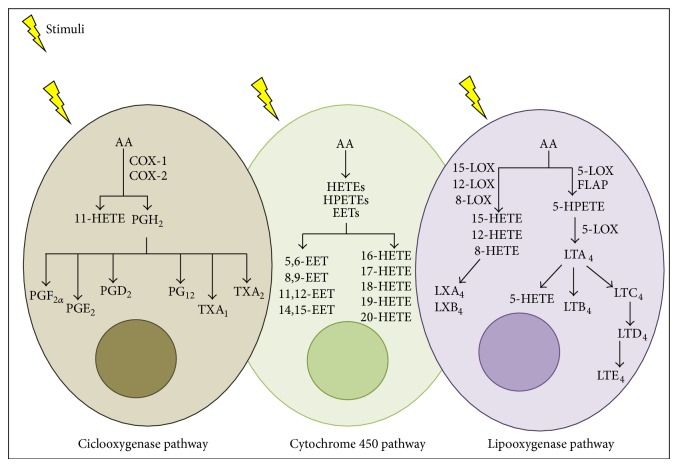
Figure 1.
Eicosanoid synthesis pathways. After cell stimulation, arachidonic acid (AA) can be metabolized by three enzymes: cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX), and cytochrome P450 (CYP 450). COX catalyzes AA in (prostaglandin) PGG2 and PGH2, and these are converted into PGD2, PGE2, PGF2α, PG12, TXA1, and TXA2. The LOX pathway catalyzes AA into hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) and diverse hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HPETEs). This pathway involves four enzymes: 5-LOX, 8-LOX, 12-LOX, and 15-LOX. 5-LOX interacts with a 5-LOX-activating protein (FLAP), enhancing the interaction of 5-LOX to AA. LTA4 hydrolases convert LTA4 into LTB4, and LTC4 synthase can convert LTA4 to LTC4, whereupon it is then metabolized to LTD4 and LTE4. 5-LOX synthetizes LXA4 and LXB4 using 15-HETE. The pathway of CYP-450 leads to the conversion of HETEs, including 16-, 17-, 18-, 19-, and 20-HETE and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): 5,6-, 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-EET.