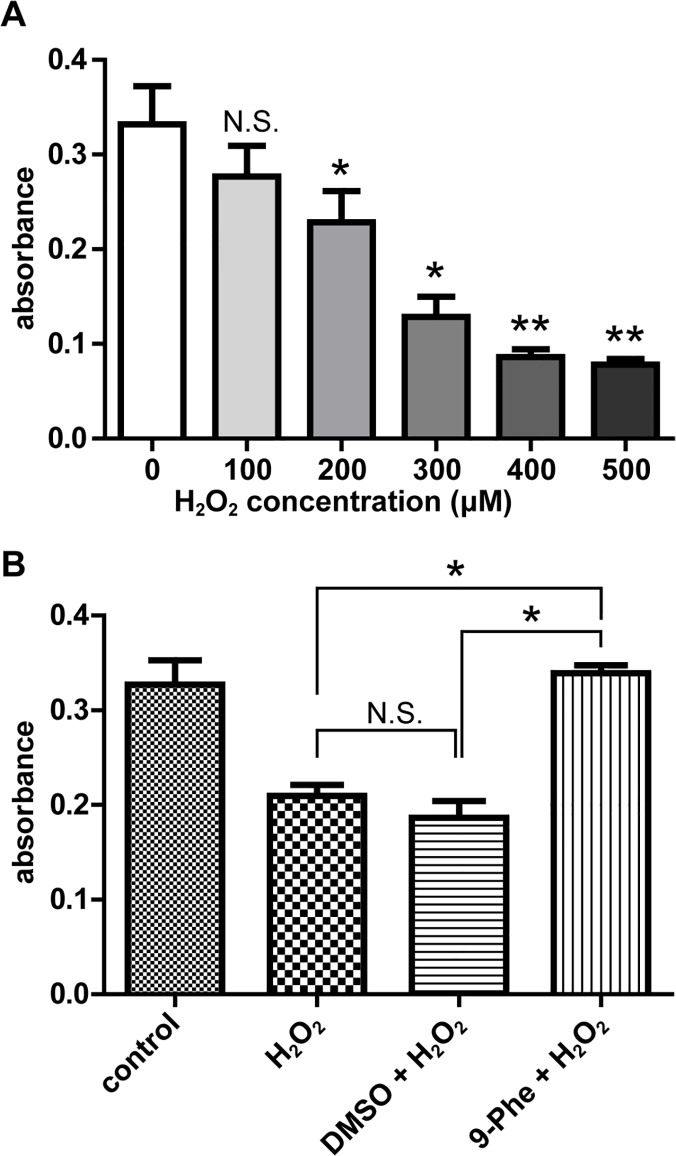
Fig 4. Protective effect of 9-Phe against H2O2-induced death in H9c2 cardiomyocytes.
(A) Dose-dependent impact of H2O2 on cell viability. Cultures of H9c2 cells were exposed 4 h to DMEM medium containing 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, or 500 μM H2O2, then viability was measured by MTT assay. Asterisks indicate significantly lower viability (absorbance) than for the control (0 μM H2O2). n = 4 for each concentration. (B) Impact of 9-Phe on the H2O2 challenge. Cultures were incubated 4 h with 200 μM H2O2 in the presence of DMSO or 20 μM 9-Phe. The 9-Phe completely prevented the damage caused by H2O2. n = 5 for each condition. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, N.S.: p > 0.05.