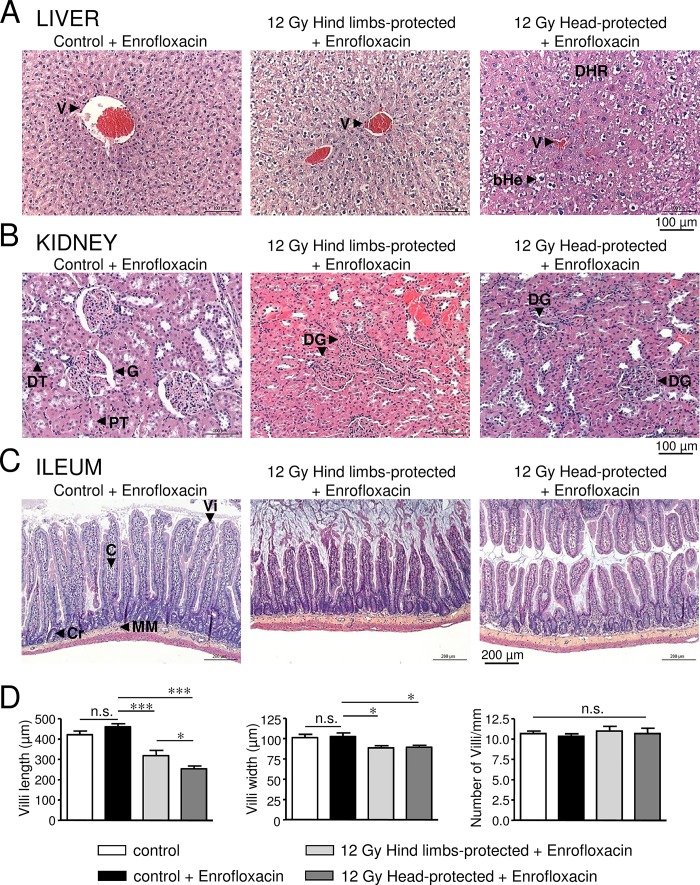
Fig 3. Histological analysis of liver, kidney and ileum damages in 12 Gy-irradiated rats with hind limbs or head protection 64 days post-irradiation.
A: Representative pictures of liver sections stained with HES for control rats and 12 Gy-irradiated rats with either hind limbs or head protection. (V: Vessel, DHR: Disorganised Hepatocyte Rows, bHe: ballooned Hepatocytes). Control and irradiated rats were treated with Enrofloxacin. B: Representative pictures of kidney sections stained with HES for control rats and 12 Gy-irradiated rats with either hind limbs or head protection. (G: Glomerulus, DG: Dysmorphic Glomerulus, PT: Proximal Tubule, DT: Distal Tubule). Control and irradiated rats were treated with Enrofloxacin. C: Representative pictures of ileum sections stained with HES for control rats and 12 Gy-irradiated rats with either hind limbs or head protection. (Vi: Villus, C: Chorion, Cr: Crypt, MM: Muscular Mucosa). Control and irradiated rats were treated with Enrofloxacin. D: Measurements of villus length/width and villus number/mm performed using ileum HES staining images. Data on left and middle graphs represent the average of 12 measurements (from 3 rats in each condition). Analysis was performed from 3 control rats, 3 control rats treated with Enrofloxacin, 3 hind limbs-protected and 3 head-protected rats irradiated at 12 Gy. Both groups of 12 Gy-Irradiated rats received Enrofloxacin treatment. (*** (p<0.001); * (p<0.05); n.s.: not significant).