Figure 2.
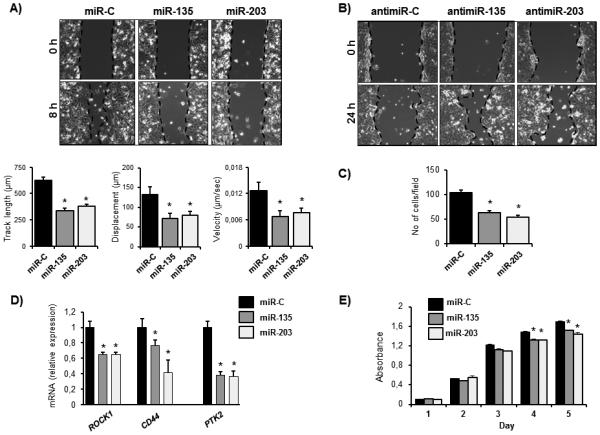
miR-135 and miR-203 suppress breast cancer cell migration and proliferation in vitro. A, MDA-MB-231-luc cells were transfected with miR-135 and miR-203 mimics or scrambled negative control miRNA (miR-C) and cell migration in wound healing assays was evaluated by live cell imaging. Migration velocity, track length, and displacement index were calculated using a velocity program, B, miRNA inhibitors (antimiR-135 and antimiR-203) and respective control antimiRNA were transfected in MCF-7 cells. Migration was evaluated in a wound-healing assay. C, miR-135, miR-203, or miR-C expressing MDA-MB-231-luc cells were subjected to a trans-well assay to evaluate chemotactic migration. D, gene expression was evaluated in miR-C miR-135 and miR-203 expressing MDA-MB-231-luc cells by qRT-PCR. Values were normalized to GAPDH. E, cell proliferation of MDA-MB-231-luc cells ectopically expressing miR-135, miR-203, or miR-C was investigated by an MTS assay. Data are represented as means ± SEM A) or ± SD (C, D, E) of each group. *significant difference compared to miR-C control (p< 0.05), Tukey’s post-hoc test.
