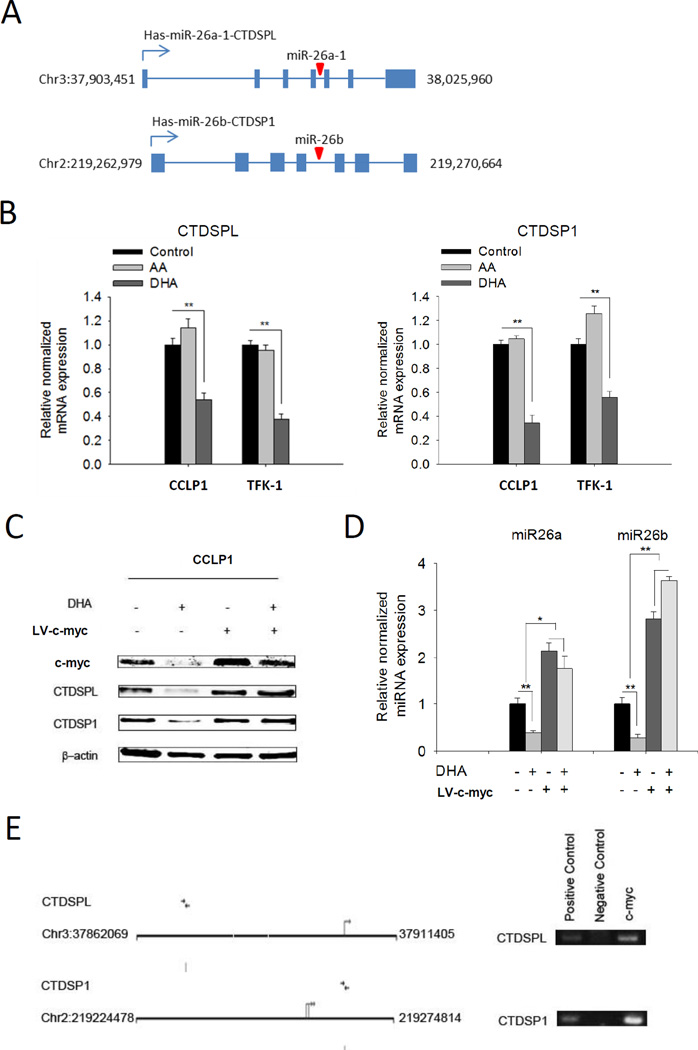
Figure 3. C-myc is implicated in ω-3 PUFA-induced suppression of miR26a/b.
(A) Schematic representation of gene map for miR26a/b and their host gene CTDSPL and CTDSP1; (B) DHA, but not AA, decreases the mRNA levels of miR26a/b host genes CTDSPL/CTDSP1 in cholangiocarcinoma cells. CCLP1 or TFK-1 cells were synchronized by serum deprivation, and then maintained in serum-free medium containing 50 µM DHA or AA for 12 h. CTDSPL or CTDSP1 mRNA was measured by real-time PCR. Results were normalized to control group; the data were shown with mean±SE. **P<0.01. (C) c-myc overexpression prevents DHA induced inhibition of CTDSPL and CTDSP1. CCLP1 cells infected with c-myc lentivirus or scramble control were maintained in serum free culture medium with or without 50 µM DHA for 12 h. Cellular proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with antibody against c-myc, CTDSPL and CTDSP1, respectively. β-actin were measured as reference gene. (D) c-myc overexpression prevents DHA induced inhibition of miR26a or miR26b. CCLP1 cells infected with c-myc lentivirus or scramble control were treated with or without 50 µM DHA for 12 h. The levels of miR26a and miR26b were measured by real-time PCR. Results were normalized to control group; data were shown with mean±SE. *P<0.05, **P<0.01; (E) c-myc binds to CTDSPL and CTDSP1 promoter region. Putative c-myc binding sites of CTDSPL and CTDSP1 promoter are shown. ChIP assay was performed by using antibody against c-myc to precipitate chromosome; antibody against Histone 3 was used as a positive control and Rabbit IgG as a negative control. Purified precipitating DNA was analyzed by PCR with primers amplifying c-myc binding regions in CTDSPL and CTDSP1 gene promoters.