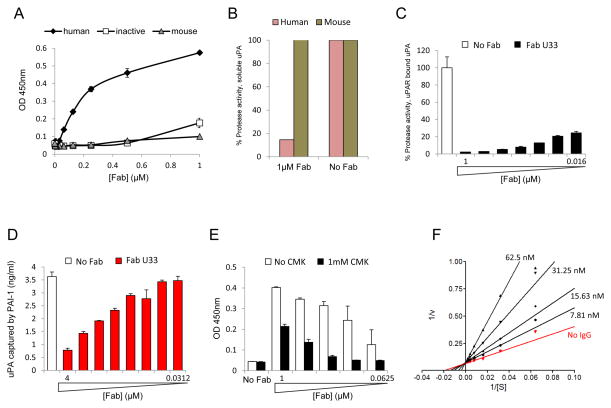
Figure 2.
Characterization of the U33 clone. (A) U33 Fab binds specifically to the active form of uPA. Serial dilutions of U33 Fab were added to uPA coated plates and incubated for 1 hour. The amount of Fab bound to uPA was determined by ELISA. U33 Fab was only detected in wells coated with human active uPA. (B) Inhibition of human uPA by U33 Fab. The proteolytic activity of human or mouse uPA was read in absence and presence of 1 μM of U33 Fab. The enzyme activity is expressed as percentage of the uPA activity in absence of Fab (100 %). (C) Inhibition of uPA bound to uPAR. Serial dilutions of U33 Fab were added to uPAR-uPA coated plates and incubated for 1 hour and the activity of uPA was read. (D) U33 Fab prevents uPA binding to PAI-1 coated plates: Serial dilutions of U33 Fab (4 μM to 31.2 nM) were pre-incubated overnight with uPA and added to PAI-1 coated plates. The amount of uPA bound to PAI was determined by ELISA. (E) U33 does not bind to uPA inhibited by a CMK inhibitor. Serial dilutions of U33 (0.0625 - 1μM) were added to an uPA coated plate pre-incubated with and without 1 μM CMK. U33 Fab bound to uPA was determined by ELISA. (F) Lineweaver-Burke plot demonstrating that U33 IgG is a competitive inhibitor of uPA.