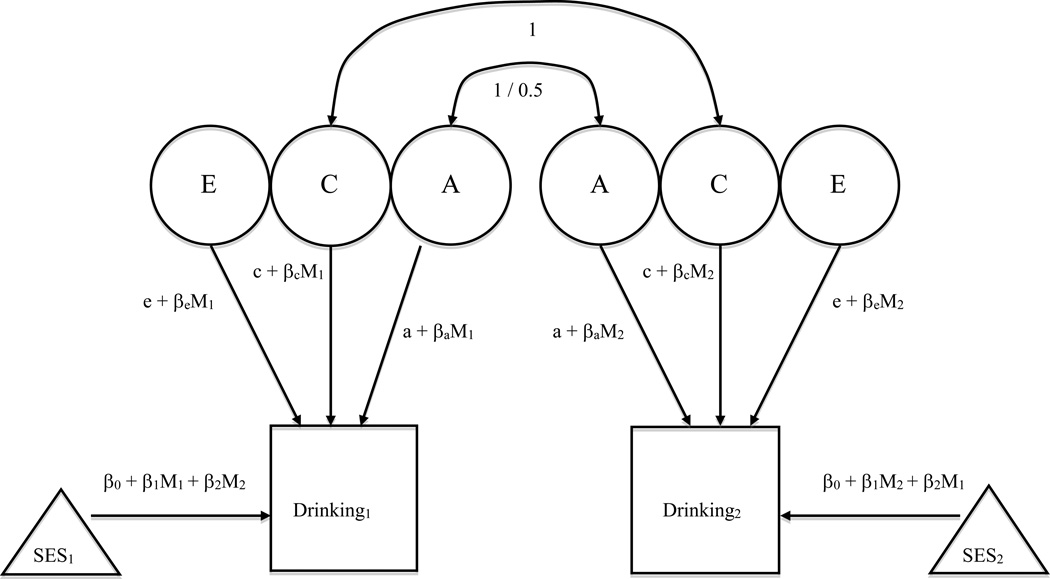
Figure 1. van der Sluis Extended Univariate Moderation Model.
The model is shown for both members of a twin pair. It allows genetic and environmental influences on Drinking to vary by the moderator M, which is socioeconomic status (SES). A, C, and E represent residual variance in Drinking after the variance in common with SES is regressed out. A represents influences due to additive genetics, C captures common/shared environmental influences, and E captures non-shared environmental influences. SES can moderate variance underlying Drinking through βa, βc, and βe, which index the direction and magnitude of genetic and environmental moderation. When these β coefficients are set to zero, this represents no moderation effects.