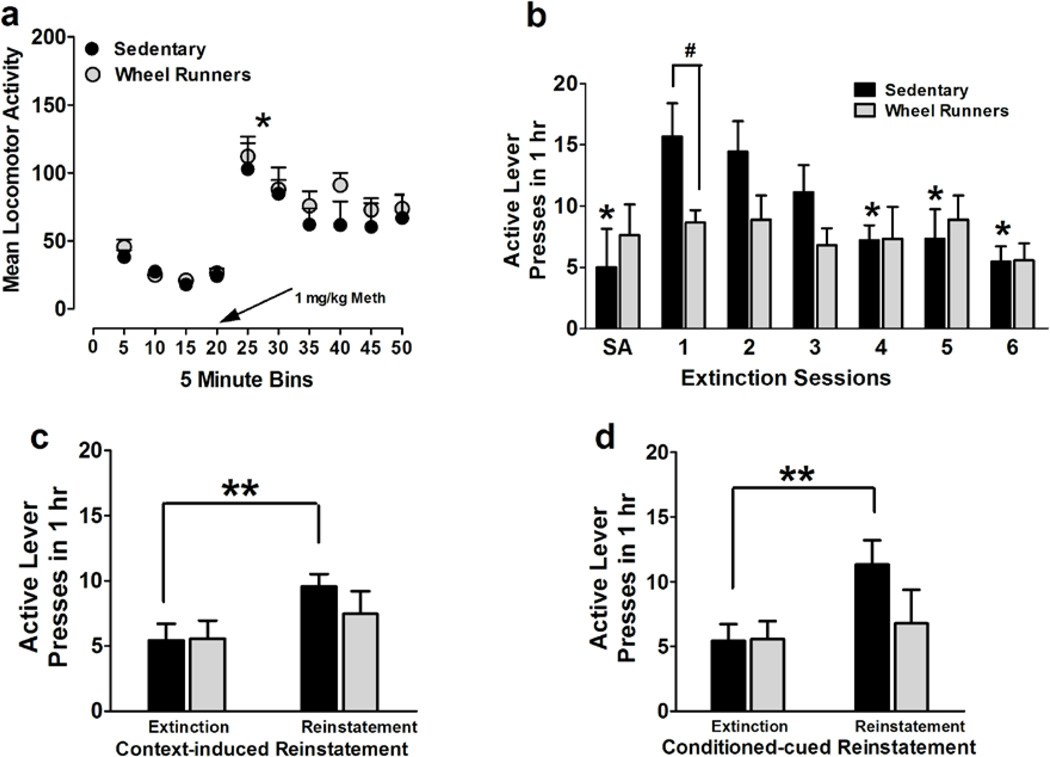
Figure 3.
(a) Locomotor activity measured as crossovers before and after an intraperitoneal injection of methamphetamine. *p<0.05 compared with activity before methamphetamine injection in sedentary and WR animals. (b–d) Extinction and reinstatement of methamphetamine seeking. (b) Increased active lever responding during first extinction session compared with the first hour responding during the last self-administration (SA) session; Decreased lever responding on the previously methamphetamine paired lever in daily 1h extinction trials in a operant box different from the one used for self-administration sessions. The extinction criterion was reached after day 4 in both groups. WR significantly reduced extinction responding compared with sedentary animals (*p≤0.05, compared with day 1 of extinction
Responding in sedentary group; # p<0.05 vs. sedentary rats). (c–d) Methamphetamine seeking triggered by context (c) and cues (d); reinstatement expressed as active lever presses. n = 9 in each group; **p<0.01, compared with extinction responding.