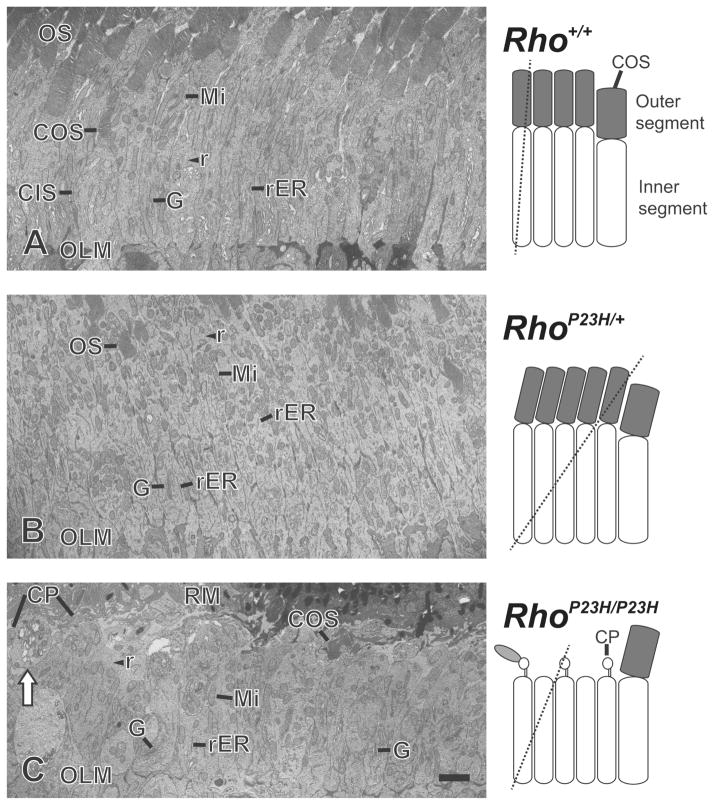
Figure 3.
Transmission electron microscopy images of photoreceptor cell inner segments at postnatal day 14. (AC) Mitochondria (Mi), rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER), Golgi apparatus (G) and ribosomes (r) were abundant in the inner segment. Golgi apparatus was observed at the proximal part of most inner segments. (A) Image of longitudinal-cut inner segments from Rho+/+ mouse retinas. Column shaped inner segments were observed between photoreceptor cell outer segments (OS) and outer limiting membranes (OLM). In rare cases, the entire cone photoreceptor outer segment (COS) and inner segment (CIS) of a single cell was observed. (B) Image of tilted-cut inner segments from RhoP23H/+ mouse retinas. 2–4 rows of oval or column shaped inner segments were observed between OS and OLM. The structure of the rER and Golgi apparatus in the inner segments of RhoP23H/+ mice was almost identical to Rho+/+ mouse retinas especially compared to tilted-cut inner segment images from Rho+/+ mouse retinas. (C) Image of slightly tilted-cut inner segments from RhoP23H/P23H mouse retinas. 1–3 rows of oval or column shaped inner segments were observed between retinal pigment epithelium microvilli (RM) and OLM. Ciliary protrusions (CP) and cone outer segments (COS) were observed in the space between RM and the distal ends of inner segments. Not all, but some inner segments showed multiple vacuolization (white arrow). Such vacuolization was observed in all four analyzed RhoP23H/P23H mice, but not in TEM images of RhoP23H/+ and Rho+/+ mice (four mice were analyzed for each genotype). Hypothetical diagram of photoreceptor cells are included, indicating the cutting planes with dashed lines. Scale bar, 2 μm.