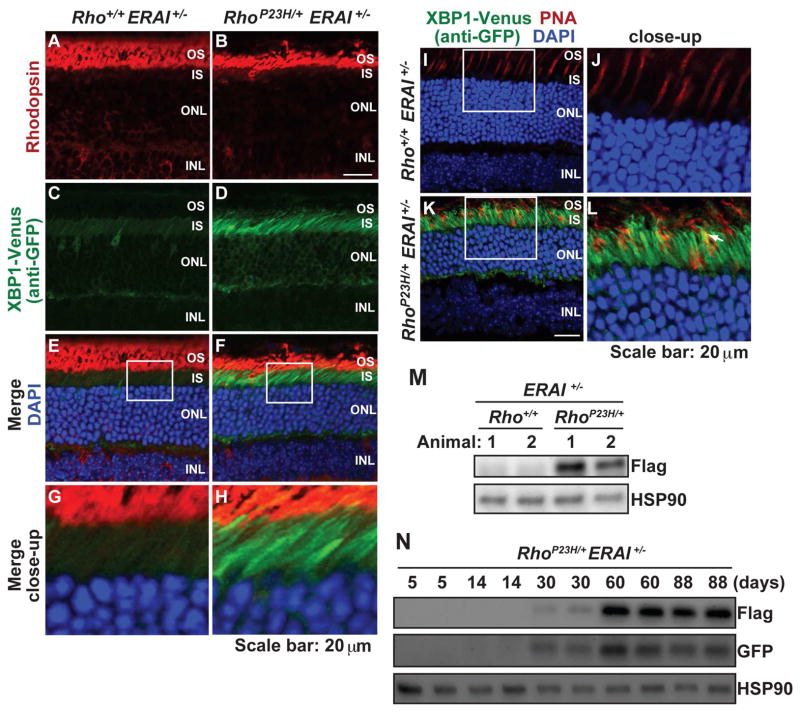
Figure 5.
The IRE1 signaling pathway of the UPR is strongly activated in photoreceptors of RhoP23H/+ERAI+/− mice. (A–H) Rhodopsin (red) and XBP1-Venus (by anti-GFP, green) were visualized in eyes from RhoP23H/+ERAI+/− mice and Rho+/+ERAI+/− mice at P30. DAPI (blue) highlights photoreceptor nuclei. Strong XBP1-Venus staining is visualized in the IS and perinuclear region of ONL photoreceptors expressing P23H rhodopsin. (I–L) Peanut agglutinin (PNA) staining of cones (red) and XBP1-Venus (by anti-GFP, green) were visualized in eyes from RhoP23H/+ERAI+/− mice and Rho+/+ERAI+/− mice at P120. DAPI (blue) highlights photoreceptor nuclei. White arrow in (L) indicated the cone cell overlapping with XBP1-Venus signal. (M) XBP1-Venus (by anti-flag) protein levels were detected in retinal lysates from RhoP23H/+ERAI+/− mice and littermate control Rho+/+ERAI+/− mice at P30. HSP90 served as a protein loading control. (N) XBP1-Venus protein levels were detected by anti-flag or anti-GFP in retinal lysates from RhoP23H/+ERAI+/− mice at indicated ages.