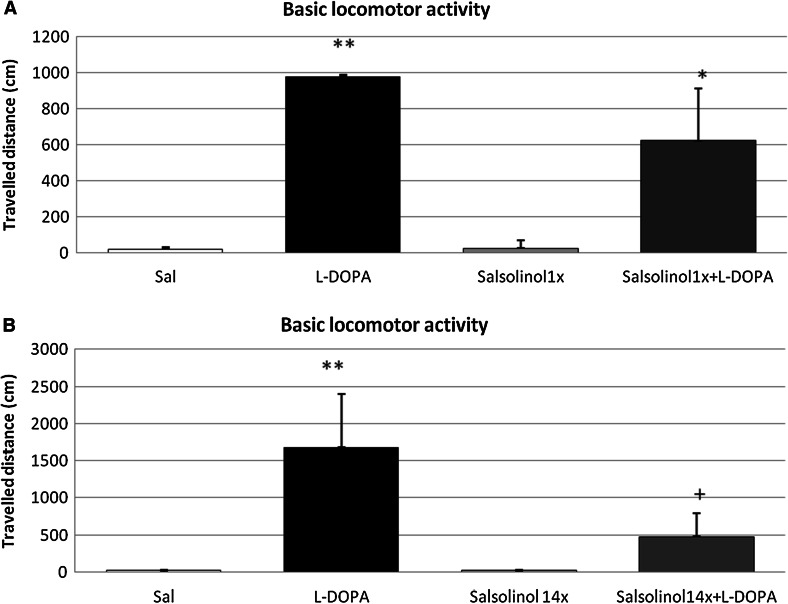
Fig. 1.
The influence of acute (a) and chronic (b) administration of salsolinol on l-DOPA-induced changes in the locomotor activity of rats. The rats were placed in actometers and, after 40 min of adaptation, received the specified drugs. Salsolinol was administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg i.p acutely (a) or chronically for 14 consecutive days (b). In the combined treatment group, l-DOPA (100 mg/kg i.p.) was administered once 15 min after final salsolinol administration. The control rats received a single injection of saline. Next, the measurement was recorded for 30 min. The data are expressed as the means ± SEM (n = 6). The data were analyzed via two-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s post hoc test when appropriate. Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus the control group; + P < 0.05 versus the l-DOPA-treated group