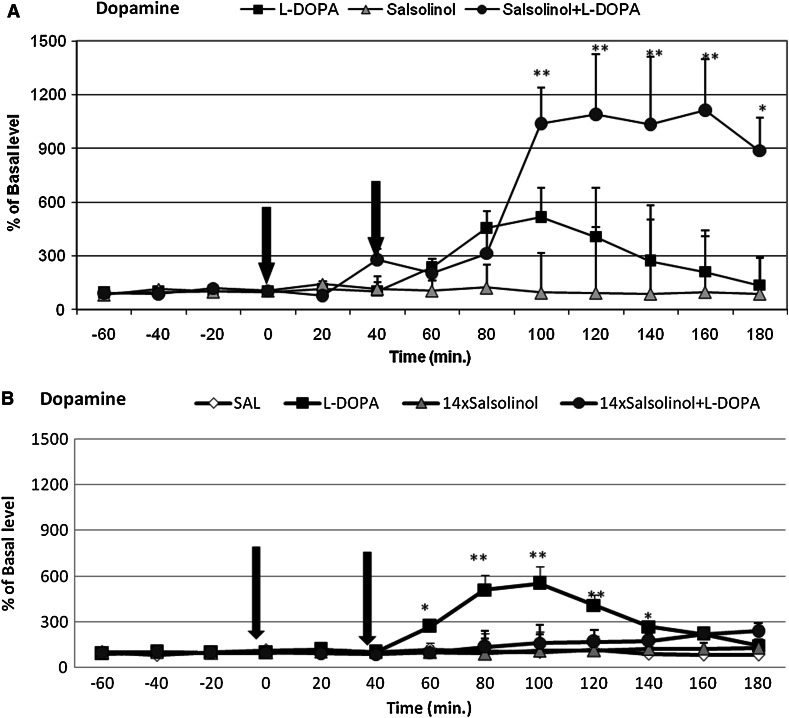
Fig. 2.
The influence of single (a) and chronic (b) administration of salsolinol on the l-DOPA-induced changes in dopamine release. Control samples were collected from “−60” to “0”; then, salsolinol (100 mg/kg; at time point “0”) or l-DOPA (100 mg/kg; at time point “40”) was administered i.p. In the combined treatment group, salsolinol was injected 40 min before l-DOPA administration (a). As shown in b, salsolinol was administered chronically at dose of 100 mg/kg i.p. for 14 consecutive days. In the combined treatment group, l-DOPA (100 mg/kg i.p.) was administered once 40 min after the final salsolinol administration. The control group was treated with saline. Dialysates were collected every 20 min. The concentration of dopamine was measured. The basal level of dopamine in the striatum was 10.6 ± 3.1 pg/20 μl. The data are expressed as the means ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus the basal level (Duncan’s test)