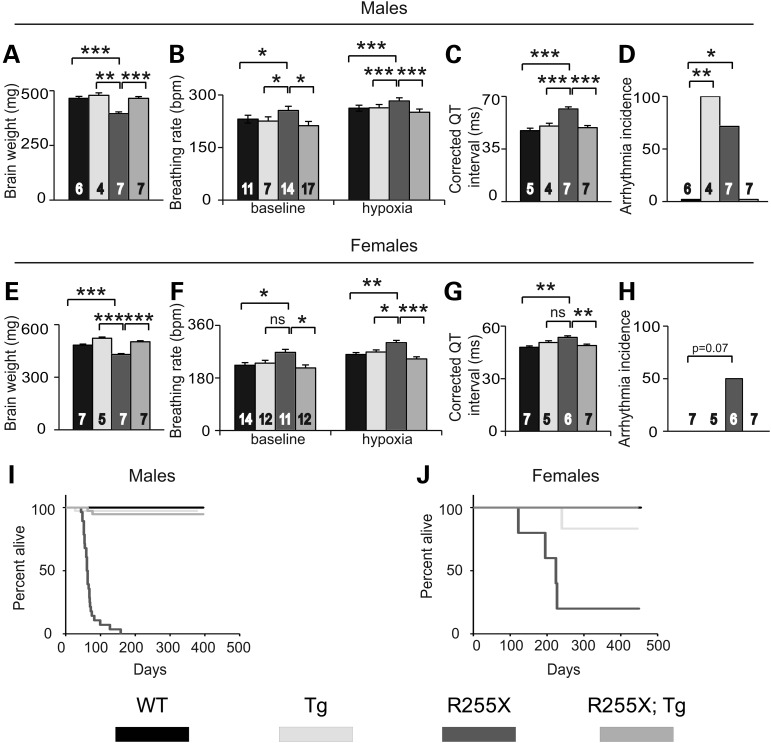
Figure 2.
R255X mice have abnormal brain, heart, breathing and weight phenotypes. (A) Mecp2R255X/Y mice have decreased brain weight compared with WT and this phenotype is rescued by MECP2Tg1. (B) Mecp2R255X/Y mice have increased breathing rate at baseline normal air conditions and when exposed to a hypoxic environment. (C) Mecp2R255X/Y have increased Q–T interval compared with WT and this phenotype is rescued by MECP2Tg1. (D) Mecp2R255X/Y has increased occurrence of arrhythmia compared with WT and this phenotype is corrected by transgene. (E) Mecp2R255X/+ mice have decreased brain weight compared with WT and this phenotype is rescued by MECP2Tg1. (F) Mecp2R255X/+ mice have increased breathing rate at baseline normal air conditions and when exposed to a hypoxic environment. (G) Mecp2R255X/+ have increased Q—T interval compared with WT and this phenotype is rescued by MECP2Tg1. (H) Mecp2R255X/+ have increased incidence of arrhythmia. (I) Male and (J) female R255X mice have reduced survival compared with WT. The premature death phenotype is rescued by MECP2Tg1. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Error bars are SEM. See Supplementary Material, Table S1 for full details regarding number of animals in each group at each age and full statistical comparisons.