Figure 1.
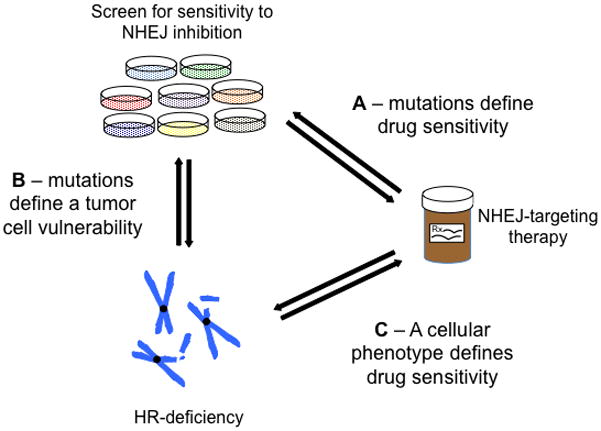
Mutually informative processes govern the use DNA repair inhibitors in repair-deficient cell lines. A) Screening for cell lines sensitive to NHEJ inhibition identifies mutations that define a set of DNA-PK-dependent tumors. B) Sensitizing mutations implicate HR-deficiency as the major defect underlying DNA-PK dependence. This suggests that other HR-mutations not found in this study may similarly sensitize tumors to DNA-PK inhibition. C) Tumor cells can similarly be defined as sensitive to a DNA-PK inhibitor or having defects in HR. This suggests that tumor cells with an HR defect – even in the absence of an HR-related mutation – would be sensitive to DNA-PK inhibition.
