Figure 4.
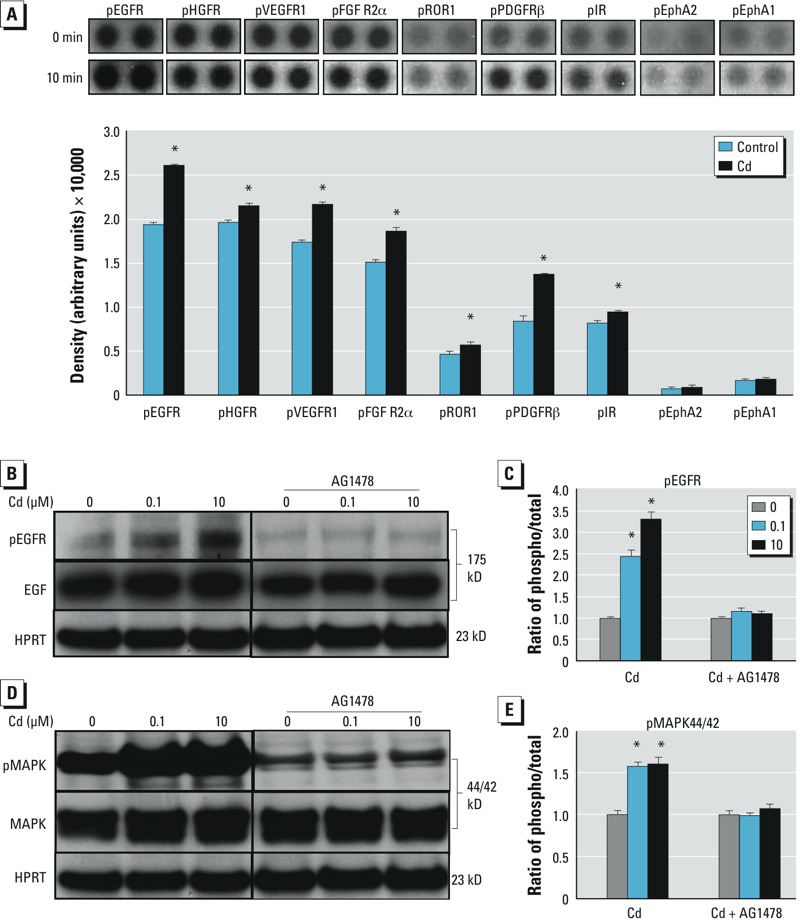
Effect of Cd on the phosphorylation (phospho) of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) as well as EGFR (pEGFR) and p44/42 MAPK (pMAPK) activation in ht-UtLM cells. (A) Expression of growth factor RTKs in ht-UtLM cells after Cd (10 μM) treatment for 10 min shown by a representative RTK array (top) and as quantitated dot blot intensity values (mean ± SE) of ht-UtLM cells (bottom). The up‑regulated RTKs were EGFR, hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR1), fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2α), receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1), platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRβ), and insulin receptor (IR); the Ephrin (Eph) receptors EphA2 and EphA1 were not significantly expressed. The array was repeated at least three times. (B–E) Effect of 0.1 or 10 μM Cd on phosphorylation of EGFR (B,C) and p44/42 MAPK (D,E) at 10 min. In the presence of AG1478 (1 μM), an EGFR inhibitor, the increased EGFR phosphorylation induced by Cd was abolished; AG1478 also abrogated Cd-induced phosphorylation of p44/42 MAPK. The experiments were repeated three times with independent cultures. *p < 0.05 compared with 0 min.
