Figure 1. The PI3K family comprises multiple classes and isoforms.
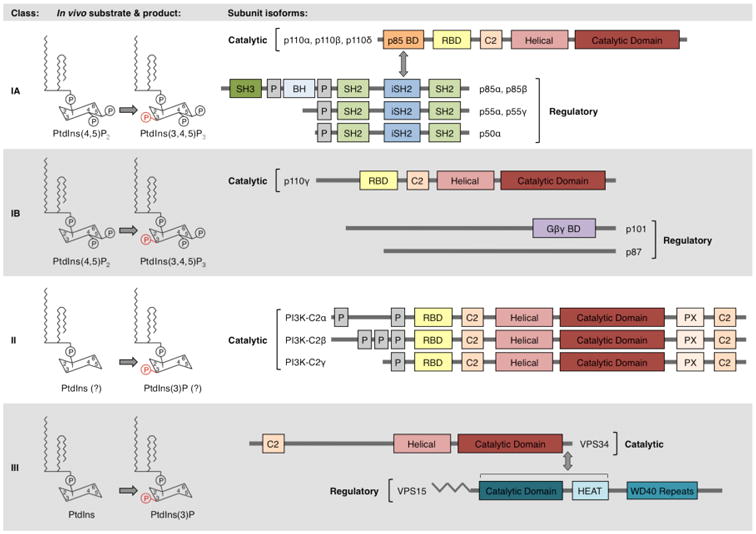
PI3Ks are classified based on their substrate specificities and structures. In vivo, class IA and IB PI3Ks phosphorylate PtdIns(4,5)P2, while class III PI3Ks phosphorylate PtdIns. Some evidence suggests that class II PI3Ks may also preferentially phosphorylate PtdIns in vivo8-10. Class IA PI3Ks are heterodimers of a p110 catalytic subunit and a p85 regulatory subunit. Class IA catalytic isoforms (p110α, p110β, and p110δ) possess a p85-binding domain (p85-BD), RAS-binding domain (RBD), helical domain, and catalytic domain. Class IA p85 regulatory isoforms (p85α, p85β, p55α, p55γ, and p50α) possess an inter-SH2 (iSH2) domain that binds class IA catalytic subunits, flanked by SH2 domains that bind phosphorylated YXXM motifs. The longer isoforms, p85α and p85β, additionally possess N-terminal SH3 and breakpoint cluster homology (BH) domains. Class IB PI3Ks are heterodimers of a p110γ catalytic subunit and a p101 or p87 regulatory subunit. p110γ possesses an RBD, helical domain, and catalytic domain. The domain structures of p101 and p87 are not fully known, but a C-terminal region of p101 has been identified as binding Gβγ subunits120. The monomeric class II isoforms (PI3K-C2α, PI3K-C2β, and PI3K-C2γ) possess an RBD, helical domain, and catalytic domain. VPS34, the only class III PI3K, possesses helical and catalytic domains. VPS34 forms a constitutive heterodimer with the myristoylated, membrane-associated VPS15 protein. Other indicated domains include proline-rich (P) domains and membrane-interacting C2 domains. Modified with permission from Reference 2.
